“Cisco,” “Critical,” “Zero-Day,” when those three words come together on an installed version of millions of routers, security professionals will have a bad day unless you tackle those vulnerabilities in your vulnerability management program. CISCO Talos has released on the 12 of October an official advisory for vulnerability CVE-2023-20198
When you add “Vulnerability,” and “Exploited” come together, it’s usually a recipe for sleepless nights for network administrators and security professionals. Unfortununately on top of that bad news nation state have also started weaponizing some of those vulnerabilities like the recent Atlassian zero day
Contents
ToggleWhy the critical Vulnerability in cisco?
CISCo IOS is a network Operating system, the gateway for all the connection in an enterprise organization and modern cloud/datacentres. In the case of the recent critical issue affecting Cisco IOS XE software, a vulnerability in the web UI feature allows remote. CISCO has advised to disable the HTTPS Server feature on all of their Internet-facing IOS XE devices to protect against a critical zero-day vulnerability in the Web User Interface of the operating system that an attacker is actively exploiting.
CVE-2023-20198: Maximum-Severity Flaw
“The vulnerability allows a remote, unauthenticated attacker to create an account on an affected system with privilege level 15 access,” Cisco said in an advisory on Oct. 16 on the new zero-day bug. “The attacker can then use that account to gain control of the affected system.” Privilege level 15 on a Cisco IOS system basically means having complete access to all commands including those for reloading the system and making configuration changes.
What are the consequences of CVE-2023-20198 on Cisco?
Tracked as CVE-2023-20198, this zero-day vulnerability impacts Cisco’s IOS XE software and has been assigned a severity rating of 10.0 on the CVSS scoring system—a perfect ten, but not the kind you want to brag about. This vulnerability affects only enterprise networking gear with the Web UI feature enabled and exposed to the internet or untrusted networks.
The flaw enables a remote attacker to create an account with privilege level 15 access without any authentication. Imagine walking into Fort Knox, and someone just hands you the keys. Tracking this vulnerability is key for your vulnerability management and prioritizing the systems that are externally facing even more priority
Recent Developments
Cisco discovered the critical flaw after spotting malicious activity on a customer device. Subsequent investigations revealed unauthorized users creating local accounts with usernames like “cisco_tac_admin” and “cisco_support”—because nothing says “suspicious” like a name that tries too hard to look legitimate.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has issued an advisory, and threat actors have reportedly exploited the vulnerability to compromise thousands of devices. Security researcher Jacob Baines eloquently summarized the situation: “This is a bad situation, as privileged access on the IOS XE likely allows attackers to monitor network traffic, pivot into protected networks, and perform any number of man-in-the-middle attacks.”
Recommendations
For those running Cisco IOS XE, it’s strongly recommended to disable the HTTP server feature on internet-facing systems. You wouldn’t leave your front door wide open; why do the equivalent with your network?
If your IOS version is vulnerable to CVE-2023-20198 and being compromised?
- Backup the configuration
- Flash IOS and recreate configuration (from backup)
For more information on cisa kev and other zero day check
How to detect CVE-2023-20198?
One method to identify if the implant is present is to run the following command against the device, where the “DEVICEIP” portion is a placeholder for the IP address of the device to check:
| curl -k -X POST “https[:]//DEVICEIP/webui/logoutconfirm.html?logon_hash=1” |
Note: The above check should use the HTTP scheme if the device is only configured for an insecure web interface.
This will request the device’s Web UI to see if the implant is present. If the request returns a hexadecimal string, like 1a80b7389ccd0a5dab, the implant is present.
Cisco has also released the following Snort coverage to address this threat. The first Snort ID is an older rule that covers CVE-2021-1435, and the last three alert if interaction with the implant occurs:
- 3:50118:2
- 3:62527:1
- 3:62528:1
- 3:62529:1
Testing for CVE-2023-20198
You can use this python script to test the scanning results and load them up in Phoenix security as results.
https://github.com/securityphoenix/cisco-CVE-2023-20198-tester
https://github.com/Shadow0ps/CVE-2023-20198-Scanner
Use the script at your own risk; feel free to edit and modify, please note all the scanners use https probe and might be illegal in your country use at your own risk
An alternative script is available here (go based)
What is the exploitation data behind CVE-2023-20198, and how widespread are those vulnerabilities?
CVSS: 10 / 9.8
CTI interest: Low 8.25 (high)
RCE Type Remote: High, Access through HTTPS port (recommended disabling) with chance of Privilege escalation
Availability: Yes
Status: Disclosed
EPSS Score: – recent addition – 0.007470000, date: 2023-10-17
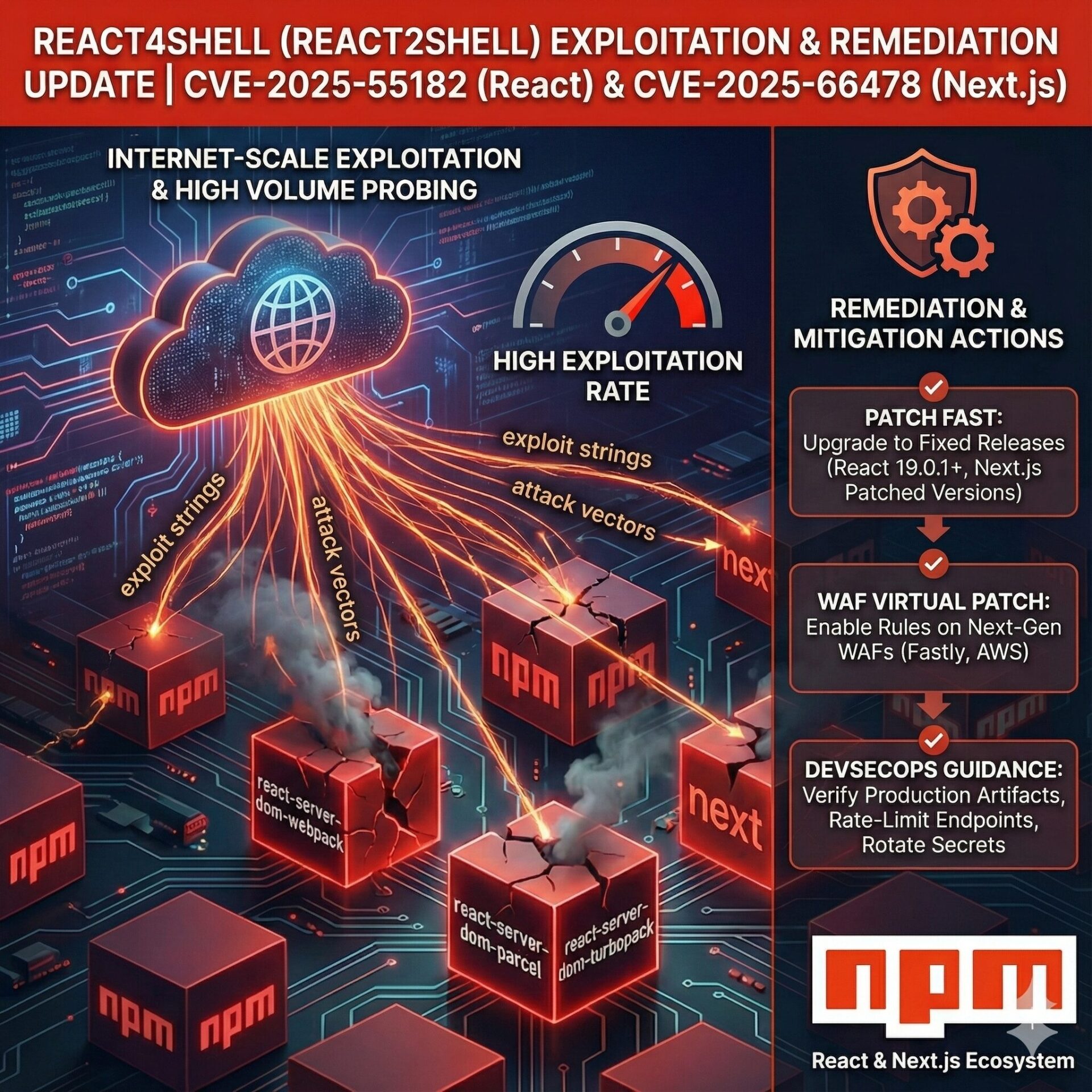
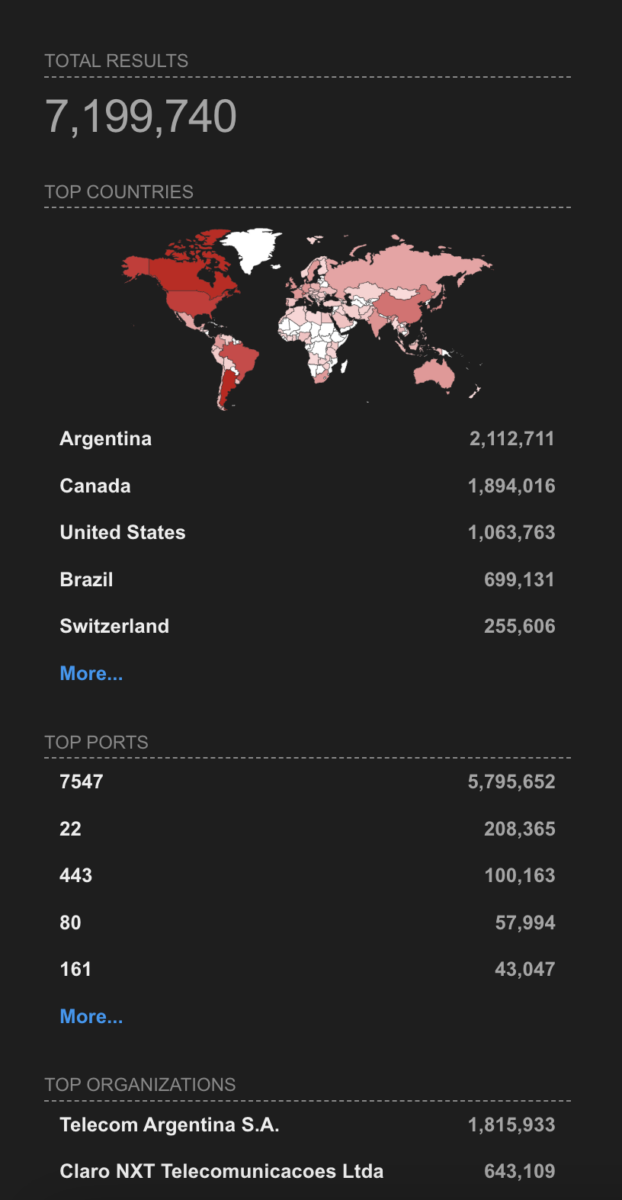
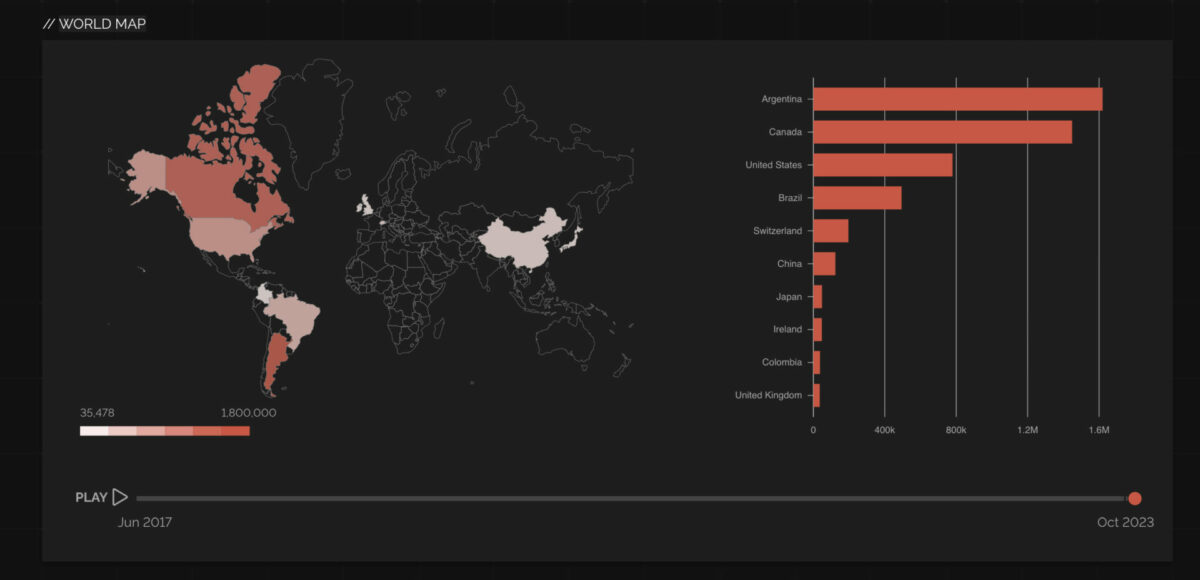
Currently, there are 1814 systems with the XE version of software and port exposed over the web with a total installation of 7M systems across the globe and 921,665 systems on IOS alone spanning from the USA to Asia. This vulnerability has a vast attack surface!


Conclusion
While the world of cybersecurity is full of noise and advisories this vulnerability advisory and alert is real. Like wargame, our resources as defenders are fairly limited and we need to understand the exposure of vulnerabilities.
How Phoenix Security Can Help

Phoenix Security helps organizations identify and trace which systems have vulnerabilities, understanding the relation between code and cloud. One of the significant challenges in securing applications is knowing where and how frameworks like Struts are used. ASPM tools can scan the application portfolio to identify instances of Struts, mapping out where it is deployed across the organization. This information is crucial for targeted security measures and efficient patch management. Phoenix Security’s robust Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) system is adept at not just managing, but preempting the exploitation of vulnerabilities through its automated identification system. This system prioritises critical vulnerabilities, ensuring that teams can address the most pressing threats first, optimising resource allocation and remediation efforts.
The Role of Application Security Posture Management (ASPM):
ASPM plays a vital role in managing and securing applications like those built with Apache Struts. It involves continuous assessment, monitoring, and improvement of the security posture of applications. ASPM tools can:
- Identify and Track Struts Components: Locate where Struts is implemented within the application infrastructure.
- Vulnerability Management: Detect known vulnerabilities in Struts and prioritize them for remediation.
- Configuration Monitoring: Ensure Struts configurations adhere to best security practices.
- Compliance: Check if the usage of Struts aligns with relevant cybersecurity regulations and standards.
By leveraging Phoenix Security, you not only unravel the potential threats but also take a significant stride in vulnerability management, ensuring your application security remains up to date and focuses on the key vulnerabilities.
Get in control of your Application Security posture and Vulnerability management
Other Resources
- Bleeping Computer · Thousands of Cisco IOS XE devices hacked in widespread attacks
- CRN · Cisco IOS XE Devices Have Been ‘Widely Exploited:’ Researcher
- The Hacker News · Warning: Unpatched Cisco Zero-Day Vulnerability Actively Targeted in the Wild
- Cybersecurity Dive · Cisco’s critical IOS XE software zero day is a ‘bad situation’
- Help Net Security · Cisco IOS XE zero-day exploited by attackers to deliver implant (CVE-2023-20198)
- CRN · Why Cisco IOS XE Attacks Are Setting Off Alarm Bells
- Security Affairs · CVE-2023-20198 ZERO-DAY WIDELY EXPLOITED TO INSTALL IMPLANTS ON CISCO IOS XE SYSTEMS
- The CyberWire · Spyware in bogus RedAlert app. Cyberespionage against ASEAN. Cisco 0-day exploited. Security-by-design. Cyber ops in Russia’s hybrid war.
- TechTarget · Cisco IOS XE zero-day facing mass exploitation
- Dark Reading · Zero-Day Alert: Thousands of Cisco IOS XE Systems Now Compromised
- Ars Technica · “Cisco buried the lede.” >10,000 network devices backdoored through unpatched 0-day
- BankInfoSecurity · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- Healthcare Info Security · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- Data Breach Today · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- Careers Info Security UK · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- Careers Info Security Asia · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- Careers Info Security India · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- Careers Info Security · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- CU Info Security · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- Info Risk Today · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- Gov Info Security · Unpatched Zero-Day Being Exploited in the Wild, Cisco Warns
- PC Mag · Critical Flaw Leads Hackers to Hijack Thousands of Cisco Devices
- Risky Biz · Risky Biz News: Mysterious APT compromises Asian government’s secure USBs
- SecurityWeek · Tens of Thousands of Cisco Devices Hacked via Zero-Day Vulnerability
- CISO Series · Cyber Security Headlines: Zero-day attacks affect 10,000 Cisco devices
- The Cyberwire · Notes from the cyber phases of two hybrid wars. Alerts on Cisco, Atlassian vulnerability exploitation. Updated guidance on security by design.
- CyberScoop · Unidentified attackers breach tens of thousands of Cisco devices
- Network Computing · Zero-Day Alert: Thousands of Cisco IOS XE Systems Now Compromised
- CRN · More Than 34,000 Cisco Devices Compromised Via IOS XE Vulnerability: Researchers
Previous Issues of Vulnerability Weekly
- How to update curl and libcurl without panic fixing
- Critical Vulnerabilities in Atlassian Confluence: Zero-Day
- Detect & Mitigate HTTP/2: Rapid Reset Vulnerabilities
- Understanding the libcue Vulnerability CVE-2023
- Understanding and fixing Curl and libcurl
- CVE-2023-3519 Update on Critical RCE in Netscaler ADC (Citrix ADC) and Netscaler Gateway (Citrix Gateway) details on vulnerability timeline and compromise
- MOVEit Transfer breach, Zellis compromise CVE-2023-34362