With a very large deployment base, the Atlassian confluence server and the new exploitation confirmed for CVE-2023-22515 CVE-2023-22518, cisa releasing an advisory in CISA KEV, have raised the alert for both the vulnerability management team and application security teams.
With the recent exploitation of Atlassian, Cisco, Curl, Http/2, F5, and many others, the end of the year feels like an endless sprint, except the hurdles are Zero-Day exploits, and the runners are cybersecurity professionals.
Data Visualization of and exploitation in various datasets and in the wild
To discover this and other vulnerabilities exploited in the wild and the data behind it explore
Recent vulnerability advisories from CISA and Microsoft have raised the alert for wide exploitation of two vulnerabilities in Atlassian servers CVE-2023-22518, and CVE-2023-22515; see all the details here to prioritize those vulnerabilities in your vulnerability management program. A new vulnerability in Atlassian’s Confluence Data Center and Server, identified as CVE-2023-22518, has been compromised by a sophisticated threat actor. Tracked as CVE-2023-22518, the vulnerability is rated 9.1 out of a maximum of 10. This vulnerability, which has the potential to cause “significant data loss,” has been further complicated by the exploitation of another severe vulnerability, CVE-2023-22515, linked to a nation-state actor known as Storm-0062 (also recognized as DarkShadow or Oro0lxy).
Microsoft has observed nation-state threat actor Storm-0062 exploiting CVE-2023-22515 in the wild since September 14, 2023. CVE-2023-22515 was disclosed on October 4, 2023. Storm-0062 is tracked by others as DarkShadow or Oro0lxy.
— Microsoft Threat Intelligence (@MsftSecIntel) October 10, 2023
All versions of Confluence Data Center and Server are susceptible to the bug, and it has been addressed in the following versions –
- 7.19.16 or later
- 8.3.4 or later
- 8.4.4 or later
- 8.5.3 or later, and
- 8.6.1 or later
Atlassian Advisories for October, including CVE-2023-22515 and CVE-2023-22518,
Atlassian has added several advisories in October:
| Security Advisory | Affected Products | Vulnerabilities |
| Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Confluence Data Center and Server | Confluence Data CenterConfluence Server | Privilege escalation (CVE-2023-22515) |
| XXE Vulnerability In Jira Service Management Data Center and Jira Service Management Server | Jira Service Management Data CenterJira Service Management Server | XXE (XML External Entity Injection) (CVE-2019-13990) |
| Improper Authorization Vulnerability in Confluence Data Center and Server | Confluence Data CenterConfluence Server | Improper Authorization (CVE-2023-22518) |
Analysis of CVE-2023-22518 Atlassian Confluence Data Centre and Server
The Emerging Threat: Atlassian’s latest security advisory has set the cybersecurity world abuzz, revealing a critical flaw in Confluence Data Center and Server that could lead to “significant data loss” in the hands of an unauthenticated attacker. This vulnerability, known as CVE-2023-22518, has been assigned a CVSS score of 9.1, placing it firmly in the “critical” category. It’s akin to discovering a hidden trapdoor in a fortress that could let invaders in, unnoticed and unchallenged.
CVE-2023-22518 is characterized as an “improper authorization vulnerability.” This flaw could potentially allow attackers to bypass security measures that are supposed to restrict access to sensitive functionalities within Confluence. For full advisory: CVE-2023-22518 – Improper Authorization Vulnerability In Confluence Data Center and Serve
A potential unverified checker for this vulnerability can be found for Scanner for CVE-2023-22518 and an alternative Scanner for CVE-2023-22515; please use those at your own risk and don’t scan assets that are not under your direct and organizational management and adhere to application security and vulnerability management best practices.
The vulnerability casts a wide net, affecting all versions of Confluence Data Center and Server up to the latest patched versions. Atlassian has swiftly provided a lifeline by releasing patches for versions 7.19.16 and above, ensuring that the door is firmly shut on this particular security risk.
Confidentiality Intact for CVE-2023-22518
In a silver lining to this cloud, Atlassian has assured users that the vulnerability does not compromise data confidentiality. This means that while the attackers might be able to cause chaos, they can’t steal the crown jewels—your data remains secure from exfiltration.
Exploitation and analysis of CVE-2023-22518
Currently, there are 164,020 servers exposed over the web, those system are often used in development and application security; since 5th of November, there has been an increase in exploitation activity of CVE-2023-22518.
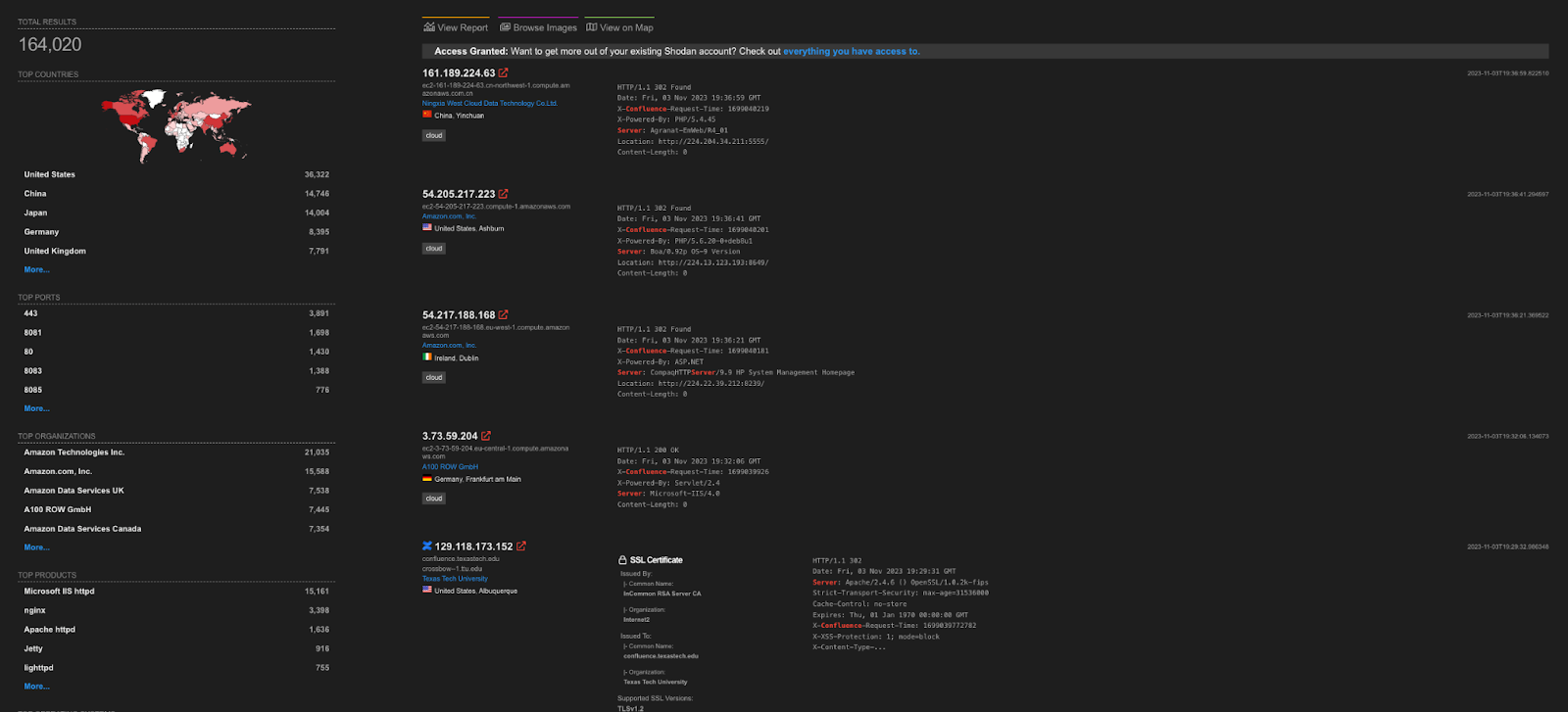
Shodan exposed Atlassian systems
Graynoise active exploitation for 2023-22518
Ransomware analysis and impact of CVE-2023-22518
CVE-2023-22518 has lead led to an attempt to deploy Cerber ransomware. The activity we observed is similar to intrusions previously reported by The DFIR Report and Rapid7.
Red Canary successfully acquired and scrutinized svcprvinit.exe, a Cerber ransomware variant, presumably originating from the leaked Conti ransomware resources. Once activated, this executable encrypts files on both local and networked storage, appends a “.LOCK3D” suffix to files, initiates a mutex for single-instance operation, eliminates volume shadow copies, leaves behind ransom instructions, and finally self-destructs.
The ransomware employs a ChaCha algorithm (an evolved version of Salsa20) for file encryption, mirroring the last identified iteration of Conti that also used ChaCha. Additionally, the malware is equipped to utilize AES and RC4 for various encryption tasks, such as key encryption.
To prevent multiple instances, the ransomware generates a mutex named “hsfjuukjzloqu28oajh727190”, a signature also noticed in other Conti-related ransomware strains, hinting at its Conti lineage. This malware is designed to encrypt a wide array of file types on both local and network drives.
Each compromised folder contains a ransom note titled “read-me3.txt”, which goes as follows:
C3RB3R GUIDELINES
IMPORTANT: KEEP THIS FILE UNTIL FULL DATA RECOVERY!
Your vital files are encrypted. Third-party restoration attempts could be disastrous! Safe decryption requires our unique “C3rb3r Decryptor”. Additionally, significant data from your system has been extracted. Failure to pay will lead to your data’s sale on the dark web.
Follow these steps to access more information on our Tor-based page:
- Download Tor browser – https://www.torproject.org/
- Install and run Tor browser
- Use the “Connect” button
- Open this link in Tor browser: http://j3qxmk6g5sk3zw62i2yhjnwmhm55rfz47fdyfkhaithlpelfjdokdxad.onion/<unique path>
- If the site isn’t loading, wait and retry
- Adhere to on-site instructions
To buy the decryptor, visit your personal page:
http://j3qxmk6g5sk3zw62i2yhjnwmhm55rfz47fdyfkhaithlpelfjdokdxad.onion/<unique path>
Here, you’ll receive detailed purchasing instructions. You can also decrypt one file for free as proof of the “C3rb3r Decryptor’s” effectiveness.
CAUTION:
- Don’t attempt file recovery solo; it can corrupt your data beyond repair.
- Internet solutions are futile; delay increases the decryption price.
- If Tor is blocked in your region or network, use it with a VPN.
The ransomware also employs cmd.exe and wmic.exe to erase volume shadow copies using this command:
cmd.exe /c C:\Windows\System32\wbem\WMIC.exe shadowcopy where “ID='<VSS ID>'” delete
Lastly, the ransomware self-eliminates using this command:
“C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe” /c del c:\windows\temp\svcprvinit.exe >> NUL
Exploitation of CVE-2023-22515:
The Exploitation by Storm-0062: Microsoft has shed light on the dark corners of the cyber world by linking the exploitation of CVE-2023-22515 directly to Storm-0062. This group, notorious for its state-sponsored activities, has been actively abusing the flaw since September 14, 2023. The critical privilege escalation vulnerability in question allows remote attackers to create unauthorized Confluence administrator accounts, giving them a skeleton key to the kingdom of Confluence servers.
A potential Scanner for Atlassian Confluence ca be found here: Scanner for CVE-2023-22515; please use those at your own risk and don’t scan assets that are not under your direct and organizational management.
The Severity of CVE-2023-22515:
With a CVSS score of a perfect 10.0, CVE-2023-22515’s severity cannot be overstated. It’s the cybersecurity equivalent of a Category 5 hurricane making landfall. Atlassian has addressed this flaw in versions 8.3.3 or later, 8.4.3 or later, and the Long Term Support release 8.5.2 or later. Despite the patch, the scale of the attacks remains as murky as London fog, with only “a handful of customers” reporting exploitation, indicating a zero-day attack by the threat actor.
Exploitation of CVE-2023-22515:
- CTI 0.08 (low)
- EPSS: Extremely high – 0.95529
- RCE Type Remote: High
- Ransomware: yes
- Exploit Availability: Yes
- Status: Disclosed
Currently, Graynoise is tracking 242 malicious attackers are exploiting this vulnerability.
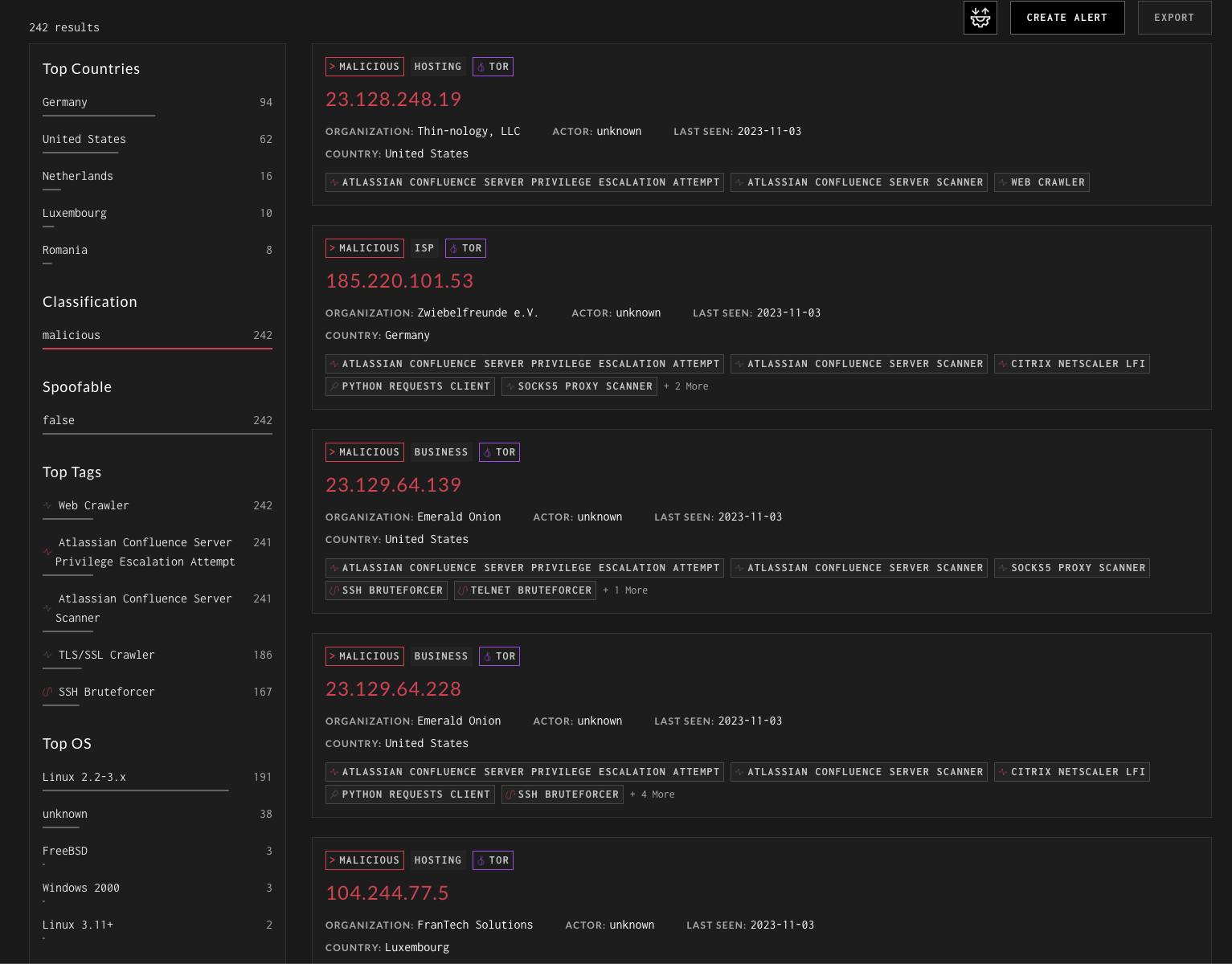
The Backstory of Oro0lxy:
Oro0lxy is not a new player on the cyber stage. This digital alias is linked to Li Xiaoyu, a Chinese hacker indicted by the U.S. Department of Justice for infiltrating numerous companies, including vaccine research entities like Moderna. Xiaoyu, along with an accomplice, is believed to be part of the Guangdong division of China’s Ministry of State Security, blending personal financial motives with state-sponsored espionage.
The Call to Action:
Organizations using Confluence as part of your application security and development must heed the call to upgrade immediately to safeguard against these vulnerabilities. Isolation from the public internet is also advised until these upgrades can be secured, echoing the cybersecurity mantra of “patch and protect.”
The Joint Advisory:
In response to the active exploitation of CVE-2023-22515, a joint cybersecurity bulletin was issued by CISA, FBI, and MS-ISAC on October 16, 2023. This advisory underscores the “widespread exploitation of unpatched Confluence instances,” a stark reminder of the vulnerability’s ease of exploitation and the urgency for organizations to act swiftly.
Conclusion:
The combined exploitation of the privilege escalation CVE-2023-22515 and CVE-2023-22518 represents toxic combination for software teams. The involvement of Storm-0062 adds a layer of geopolitical intrigue and complexity to the already challenging task of vulnerability management.
As cybersecurity professionals, we must not only respond to these threats with technical acumen but also with prioritized outcomes and an understanding of the broader cyber-political landscape. Let’s ensure our defences are as robust as the British spirit during a storm—unyielding and resolute.
Let’s remember that the only thing more resilient than our defences should be our resolve to maintain them. The only constant where we live in is change, and the only effective response is rapid identification of what to fix. So, let’s adapt, overcome, and keep our digital realms as secure as the Crown Jewels.
How Phoenix Security Can Help

Phoenix Security helps organizations identify and trace which systems have vulnerabilities, understanding the relation between code and cloud. One of the significant challenges in securing applications is knowing where and how frameworks like Struts are used. ASPM tools can scan the application portfolio to identify instances of Struts, mapping out where it is deployed across the organization. This information is crucial for targeted security measures and efficient patch management. Phoenix Security’s robust Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) system is adept at not just managing, but preempting the exploitation of vulnerabilities through its automated identification system. This system prioritises critical vulnerabilities, ensuring that teams can address the most pressing threats first, optimising resource allocation and remediation efforts.
The Role of Application Security Posture Management (ASPM):
ASPM plays a vital role in managing and securing applications like those built with Apache Struts. It involves continuous assessment, monitoring, and improvement of the security posture of applications. ASPM tools can:
- Identify and Track Struts Components: Locate where Struts is implemented within the application infrastructure.
- Vulnerability Management: Detect known vulnerabilities in Struts and prioritize them for remediation.
- Configuration Monitoring: Ensure Struts configurations adhere to best security practices.
- Compliance: Check if the usage of Struts aligns with relevant cybersecurity regulations and standards.
By leveraging Phoenix Security, you not only unravel the potential threats but also take a significant stride in vulnerability management, ensuring your application security remains up to date and focuses on the key vulnerabilities.
Get in control of your Application Security posture and Vulnerability management
Previous Issues of Vulnerability Weekly
- Critical vulnerability F5
- How to update curl and libcurl without panic fixing
- Critical Vulnerabilities in Atlassian Confluence: Zero-Day
- Detect & Mitigate HTTP/2: Rapid Reset Vulnerabilities
- Understanding the libcue Vulnerability CVE-2023
- Understanding and fixing Curl and libcurl
- CVE-2023-3519 Update on Critical RCE in Netscaler ADC (Citrix ADC) and Netscaler Gateway (Citrix Gateway) details on vulnerability timeline and compromise
- MOVEit Transfer breach, Zellis compromise CVE-2023-34362
Other Useful resources
Data Visualization of vulnerabilities in the wild
CISA KEV: https://phoenix.security/what-is-cisa-kev-main/
Exploit in the wild: https://phoenix.security/what-is-exploitability/
OWASP/Appsec Vulnerability: https://phoenix.security/what-is-owasp-main/
CWE/Appsec Vulnerabilities: https://phoenix.security/what-is-cwe-main/