
SysAid, which is a vendor for IT management software, has published a critical warning regarding an unpatched bug in its on-site service software version in November 6th, 2023. Recently uncovered as SANS vulnerability id CVE-2023-47246, this is vulnerability has already become exploitable in the wild. To start with, Microsoft identified and disclosed this vulnerability, attributing it to ransomware gang TA505 commonly known as Lace Tempest or cl0p.
Lace Tempest, which is known for distributing the Cl0p ransomware, has in the past leveraged zero-day flaws in MOVEit Transfer and PaperCut servers.
Data Visualization of and exploitation in various datasets and in the wild
To discover this and other vulnerabilities exploited in the wild and the data behind it explore
CVE-2023-47246 in details
This is an example of a path traversal vulnerability leading to code execution in SysAid’s on-premises software, identified as CVE-2023-47246. For instance, it offers attackers an opportunity to create a WAR file webshell and other forms of payload that are executed in the SysAid Apache Tomcat webserver. A notable indication of the breach is the presence of a webshell in the directory C: \Program Files\SysAidServer\tomcat\webapps\usersfiles.
“After exploiting the vulnerability, Lace Tempest issued commands via the SysAid software to deliver a malware loader for the Gracewire malware,” Microsoft.
Microsoft has discovered exploitation of a 0-day vulnerability in the SysAid IT support software in limited attacks by Lace Tempest, a threat actor that distributes Clop ransomware. Microsoft notified SysAid about the issue (CVE-2023-47246), which they immediately patched.
— Microsoft Threat Intelligence (@MsftSecIntel) November 9, 2023
According to SysAid, the threat actor has been observed uploading a WAR archive containing a web shell and other payloads into the webroot of the SysAid Tomcat web service.
Decoding CVE-2023-47246 and its impact in the wild of the zero-day vulnerability
- CVSS (rescored) 5.5
- CTI – 0.4 (low use)
- Impact – High (ransomware)
- EPSS – 0.000460000 (very low)
- Exploit Available / Used for ransomware
Shdan distribution
The distribution in Shodan is relatively small 869 servers with a variation between 230 instances that are accessible on the public internet and 900 with those two queries SysAId and SysAid Help desk
Currently, there are no indicators of exploitation in mass for this vulnerability so the risk level remains moderate,; as this vulnerability is used for ransomware attacks is suggested to patch
The popularity of the vulnerability has decreased since the publication on the 11 and the initial advisory.
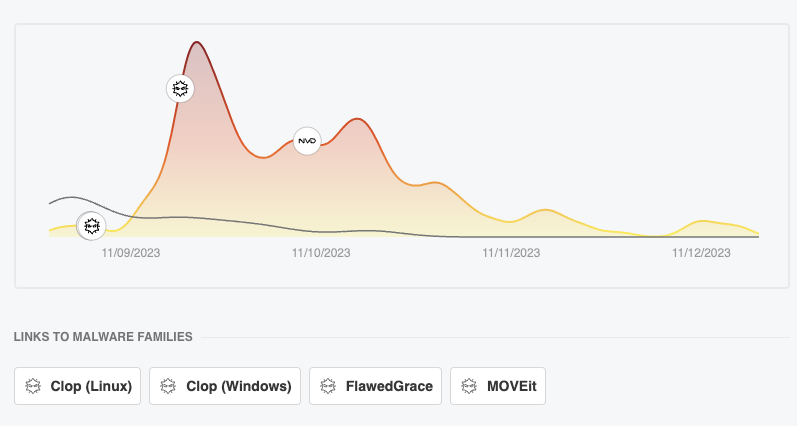
Feedly CVE analysis
The vulnerability is critical as it opens a web shell and back door for further exploitation.
The web shell, besides providing the threat actor with backdoor access to the compromised host, is used to deliver a PowerShell script that’s designed to execute a loader that, in turn, loads Gracewire.
Also deployed by the attackers is a second PowerShell script that’s used to erase evidence of the exploitation after the malicious payloads have been deployed. Furthermore, the attack chains are characterised by the use of the MeshCentral Agent as well as PowerShell to download and run Cobalt Strike, a legitimate post-exploitation framework.
“As of June 2023, the Silent Ransom Group (SRG), also called Luna Moth, conducted callback phishing data theft and extortion attacks by sending victims a phone number in a phishing attempt, usually relating to pending charges on the victims’ account,” FBI said.
Fixes for CVE-2023-47246:
SysAid’s response, a patch in version 23.3.36, is a critical first step. However, the responsibility doesn’t end there. Organizations must ensure they are updated to this latest version to mitigate the risk. Huntress, for its part, has updated its security platform to detect activities related to this exploit, offering an extra layer of defense.
Indicators of Compromise CVE-2023-47246
| Path | SHA256 Hash |
| C:\Program Files\SysAidServer\tomcat\webapps\usersfiles\user.exe | b5acf14cdac40be590318dee95425d0746e85b1b7b1cbd14da66f21f2522bf4d |
| C:\Program Files\SysAidServer\tomcat\webapps\usersfiles.war | 5ac0a6c76160772acd8a0de0705362fcdc325138eeadfe3d8d40e4bf2212a146 |
How Phoenix Security Can Help

Phoenix Security helps organizations identify and trace which systems have vulnerabilities, understanding the relation between code and cloud. One of the significant challenges in securing applications is knowing where and how frameworks like Struts are used. ASPM tools can scan the application portfolio to identify instances of Struts, mapping out where it is deployed across the organization. This information is crucial for targeted security measures and efficient patch management. Phoenix Security’s robust Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) system is adept at not just managing, but preempting the exploitation of vulnerabilities through its automated identification system. This system prioritises critical vulnerabilities, ensuring that teams can address the most pressing threats first, optimising resource allocation and remediation efforts.
The Role of Application Security Posture Management (ASPM):
ASPM plays a vital role in managing and securing applications like those built with Apache Struts. It involves continuous assessment, monitoring, and improvement of the security posture of applications. ASPM tools can:
- Identify and Track Struts Components: Locate where Struts is implemented within the application infrastructure.
- Vulnerability Management: Detect known vulnerabilities in Struts and prioritize them for remediation.
- Configuration Monitoring: Ensure Struts configurations adhere to best security practices.
- Compliance: Check if the usage of Struts aligns with relevant cybersecurity regulations and standards.
By leveraging Phoenix Security, you not only unravel the potential threats but also take a significant stride in vulnerability management, ensuring your application security remains up to date and focuses on the key vulnerabilities.
Get an overview of your asset lineage
Previous Issues of Vulnerability Weekly
- Apache Active MQ
- Atlassian Critical Vulnerability Exploited by nation-state CVE-2023-22515
- Critical vulnerability F5
- How to update curl and libcurl without panic fixing
- Critical Vulnerabilities in Atlassian Confluence: Zero-Day
- Detect & Mitigate HTTP/2: Rapid Reset Vulnerabilities
- Understanding the libcue Vulnerability CVE-2023
- Understanding and fixing Curl and libcurl
- MOVEit Transfer breach, Zellis compromise CVE-2023-34362
Other Useful resources
Data Visualization of vulnerabilities in the wild
- CISA KEV: https://phoenix.security/what-is-cisa-kev-main/
- Exploit in the wild: https://phoenix.security/what-is-exploitability/
- OWASP/Appsec Vulnerability: https://phoenix.security/what-is-owasp-main/
- CWE/Appsec Vulnerabilities: https://phoenix.security/what-is-cwe-main/














