Apache Struts 2 exploitation is in the wild; we have previously explored the details of CVE-2023-50164 in several advisories (akamai, shadow server) with evidence of exploits for CVE-2023-50164, a critical vulnerability; currently, it is a perfect 9.8. The library is integrated into many systems and was previously known for the infamous Equifax breach affecting the organization’s application security program an ASPM product can help control the attack surface before and after deployment.
identified as CVE-2023-50164, has taken a critical turn; this flaw exists in the Apache Struts 2 framework’s “file upload logic.” It allows unauthorized path traversal, enabling attackers to upload and execute malicious files remotely. Despite the complexity of the attack, there is mounting evidence of exploitation in the wild, underscoring the urgent need for effective vulnerability management strategies.
What is Apache Struts, and what affects CVE-2023-50164?
Apache Struts is an open-source framework used for developing Java EE web applications. It employs the Model-View-Controller (MVC) paradigm, enabling developers to create applications that separate display, logic, and data components. Struts have been pivotal in the development landscape, offering an extensible architecture and a robust set of tools and integrations.
Location and Usage in Web Applications for Apache Struts
Struts are typically located at the core of a web application’s architecture. It interacts with Java Servlets and JavaServer Pages (JSP) to process web requests, render responses, and manage application flow. Struts is widely used across various industries due to its efficiency in building scalable, reliable, and maintainable web applications.
The Impact of Struts Vulnerability CVE-2023-50164:
The impact of vulnerabilities in Struts, especially those leading to remote code execution, is profound. These flaws can allow unauthorized access to web servers, enabling attackers to manipulate or steal sensitive data, disrupt services, or use compromised systems for further attacks. High-profile breaches, like the Equifax incident, underscore the potential damage from exploiting Struts vulnerabilities.
Emergence of New Exploitation Tactics: Recent developments have revealed that the proof of concept (PoC) for CVE-2023-50164 is now publicly available, leading to increased attempts at exploiting this flaw. This vulnerability in Apache Struts 2, a popular open-source framework for building enterprise-level Java web applications, allows for remote code execution through file upload manipulation.
How to Remediate
The Apache Struts project urges to perform mitigation to the vulnerability by upgrading to one of the patched versions:
Get an overview of your asset lineage
Exploitation and analysis of CVE-2023-50164
Rising Concerns and Exploits in the Wild: The cybersecurity community is witnessing a surge in exploit attempts, even though executing these attacks is considered to have a high level of complexity. This uptick in activities suggests that threat actors are actively seeking to leverage this vulnerability, putting countless systems and data at risk.
Vendors Like Cisco Facing Increased Vulnerability: Prominent tech vendors, such as Cisco, have reported numerous products potentially vulnerable to CVE-2023-50164. This revelation highlights the widespread impact of the flaw across various network management and communication tools, intensifying the call for immediate remedial actions. An ASPM product that control attack surface can help in those situation

Currently, there are 4315 servers exposed, with Apache struts servers exposed over the web; there is currently no exploitation activity for this vulnerability nor evidence of exploitation. Nonetheless, as the previous effect of struts we recommend caution and quick update.
EPSS Score for the vulnerability is still low as it was just disclosed (0.00142) further down the week the exploitation got corrected to 0.097990000
Despite being highly popular as the package is in the most common web servers, the vulnerability has been classified.
- Common in enterprise
- Difficult to weaponize,
- Vulnerable in uncommon configuration
Exploitation Attempts for CVE-2023-50164 in Apache Struts
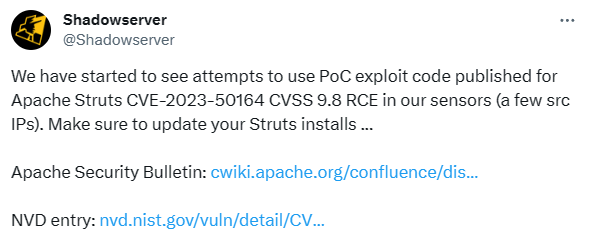
Early exploitation from Shadowserver leads to evidence of some IP addresses involved in exploitation attempts for CVE-2023-50164 vulnerability. There is also evidence of PoC from the original post https://xz.aliyun.com/t/13172 . However, exploitation of this vulnerability will be target-specific based on the differing target action’s endpoints, the naming convention of the expected uploaded file name, and any other target-specific restrictions that may need to be overcome; hence, the vulnerability exploitation remains low.
References for CVE-2023-50164 in Apache Struts
CVE-2023-50164 (https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2023-50164)
Exploit
https://github.com/jakabakos/CVE-2023-50164-Apache-Struts-RCE
Miscellaneous
https://lists.apache.org/thread/yh09b3fkf6vz5d6jdgrlvmg60lfwtqhj
http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2023/12/07/1
https://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2023/12/07/1
Technical Analysis (https://xz.aliyun.com/t/13172)
http://packetstormsecurity.com/files/176157/Struts-S2-066-File-Upload-Remote-Code-Execution.html
https://security.netapp.com/advisory/ntap-20231214-0010/
First Supply chain victim of Apache 2 struts vulnerability CVE-2023-50164
Cisco, a leading player in the tech industry, has issued a critical security advisory highlighting its investigation into the impact of the Apache Struts vulnerability on its suite of products. In a security advisory, the company disclosed an ongoing investigation to identify affected products and assess the impact. This probe underlines the far-reaching consequences of the widely-used Apache Struts framework in major tech infrastructures. Particularly under Cisco’s lens are key solutions like the Cisco Customer Collaboration Platform (formerly known as SocialMiner), Identity Services Engine (ISE), and a range of products in network management, voice, and unified communications sectors.
As the investigation progresses, Cisco is committed to regularly updating its security advisory, promising to provide detailed Cisco bug IDs for each impacted product. These updates will be crucial for users, as they will also offer insights into available patches and potential workarounds, ensuring heightened cybersecurity and resilience against such vulnerabilities. Stay tuned for Cisco’s crucial updates to safeguard your network and communication systems.
Urgent Call to Action: Patching is Imperative: Apache released patches for CVE-2023-50164 in response to these threats on December 7. To safeguard against these growing exploitation attempts, users are strongly recommended to update to the secured versions of Struts – specifically, Struts 2.5.33 or Struts 6.3.0.2, or later. This patching is a precaution and a necessity in the current threat landscape.
Patch Analysis for CVE-2023-50164
- Two commits are highlighted as particularly relevant:
- “Always delete uploaded file” ensures temporary files are correctly deleted after upload. Before the patch, overly long file upload parameters could leave temporary files on the disk.
- “Makes HttpParameters case-insensitive” changes how the
HttpParametersclass handles parameter names, treating them as case-insensitive.
The Equifax data breach linked to struts.
Equifax in 2017, which resulted from the exploitation of a known vulnerability in the Apache Struts framework. An ASPM and SCA could have helped accelerate the identification of the vulnerable systems. Here are the key points:
- Cause of the Breach: The Equifax data breach, which exposed sensitive data of approximately 143 million people, was caused by exploiting a flaw in the Apache Struts framework. Notably, Apache had already patched this flaw over two months before the breach occurred.
- Vulnerability Details: The specific vulnerability exploited in the Equifax breach was identified as CVE-2017-5638 in Apache Struts2. This was a critical vulnerability with a maximum score of 10.0. Apache had disclosed and fixed this vulnerability on March 6 by releasing Apache Struts version 2.3.32 or 2.5.10.1.
- Nature of the Flaw: CVE-2017-5638 was a remote code execution bug located in the Jakarta Multipart parser of Apache Struts2. It allowed attackers to execute malicious commands on the server during file uploads. The vulnerability could be exploited by sending a specially crafted request with a malicious ‘Content-Type’ value.
- Delayed Patching: Despite the availability of patches and evidence that the flaw was actively exploited by hackers, Equifax failed to update its web applications against this flaw, leading to the data breach.
- Equifax’s Response: After the breach, Equifax conducted an intense investigation with the aid of a cybersecurity firm to determine the scope of the intrusion and the information accessed. They confirmed that the breach exploited the Apache Struts CVE-2017-5638 vulnerability and continued to work with law enforcement on the criminal investigation.
- Widespread Use of Apache Struts: Apache Struts is a popular open-source MVC framework for Java web applications, used by many Fortune 100 companies. The widespread use of this framework meant that the vulnerability had a significant potential impact across various industries.
- Follow-Up Measures: Following the breach, Equifax offered free credit-monitoring and identity theft protection services to affected individuals. They also implemented a security freeze for accessing personal information and updated their PIN generation method for added security.
How Phoenix Security Can Help

Phoenix Security ASPM helps organizations identify and trace which systems have vulnerabilities, understanding the relation between code and cloud. One of the significant challenges in securing applications is knowing where and how frameworks like Struts are used. ASPM tools can scan the application portfolio to identify instances of Struts, mapping out where it is deployed across the organization. This information is crucial for targeted security measures and efficient patch management. Phoenix Security’s robust Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) system is adept at not just managing, but preempting the exploitation of vulnerabilities through its automated identification system. This system prioritises critical vulnerabilities, ensuring that teams can address the most pressing threats first, optimising resource allocation and remediation efforts.

The Role of Application Security Posture Management (ASPM):
ASPM is vital in managing and securing applications like those built with Apache Struts. It involves continuous assessment, monitoring, and improvement of the security posture of applications. ASPM tools can:
- Identify and Track Struts Components: Locate where Struts is implemented within the application infrastructure.
- Vulnerability Management: Detect known vulnerabilities in Struts and prioritize them for remediation.
- Configuration Monitoring: Ensure Struts configurations adhere to best security practices.
- Compliance: Check if the usage of Struts aligns with relevant cybersecurity regulations and standards.

By leveraging Phoenix Security, you not only unravel the potential threats but also take a significant stride in vulnerability management, ensuring your application security remains up to date and focuses on the key vulnerabilities.
Get an overview of your asset lineage
Previous Issues of Vulnerability Weekly
- Apache Active MQ
- Atlassian Critical Vulnerability Exploited by nation-state CVE-2023-22515
- Critical vulnerability F5
- How to update curl and libcurl without panic fixing
- Critical Vulnerabilities in Atlassian Confluence: Zero-Day
- Detect & Mitigate HTTP/2: Rapid Reset Vulnerabilities
- Understanding the libcue Vulnerability CVE-2023
- Understanding and fixing Curl and libcurl
- MOVEit Transfer breach, Zellis compromise CVE-2023-34362
Other Useful resources
Data Visualization of vulnerabilities in the wild
- CISA KEV: https://phoenix.security/what-is-cisa-kev-main/
- Exploit in the wild: https://phoenix.security/what-is-exploitability/
- OWASP/Appsec Vulnerability: https://phoenix.security/what-is-owasp-main/
- CWE/Appsec Vulnerabilities: https://phoenix.security/what-is-cwe-main/