Atlassian Confluence is a cornerstone for every developer; CISA has recently announced that Confluence, a popular tool for documentation and application security, has recently been under the spotlight due to a series of critical vulnerabilities CVE-2023-21715 in particular. With nation-state actors increasingly exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities, it’s crucial to stay updated. This blog post aims to answer key questions about some of the most recent vulnerabilities affecting Atlassian Confluence. Atlassian has released an advisory for CVE-2023-22515
—-
Contents
TogglePrevious Issues of Vulnerability Weekly
- How to update curl and libcurl without panic fixing
- Critical Vulnerabilities in Atlassian Confluence: Zero-Day
- Detect & Mitigate HTTP/2: Rapid Reset Vulnerabilities
- Understanding the libcue Vulnerability CVE-2023
- Understanding and fixing Curl and libcurl
- CVE-2023-3519 Update on Critical RCE in Netscaler ADC (Citrix ADC) and Netscaler Gateway (Citrix Gateway) details on vulnerability timeline and compromise
- MOVEit Transfer breach, Zellis compromise CVE-2023-34362
—-
What is the CVE-2023-21715 Vulnerability?
CVE-2023-22515 is a critical zero-day vulnerability affecting publicly exposed instances of Confluence Data Center and Server from version 8 on.
A remote, unauthenticated attacker could exploit this privilege escalation to create unauthorized Confluence administrator accounts and access Confluence servers. Exploitation does not require user interaction and is easy to execute.
The confidentiality, integrity and availability of information are impacted to the highest degree.
Atlassian Confluence vulnerabilities refer to security flaws in the Confluence Data Center and Server that can be exploited to gain unauthorized access see vulnerabilities part of your Application Security program, manipulate data, or perform other malicious activities. These vulnerabilities are often critical and require immediate attention.
How Secure is Atlassian Confluence?
Atlassian Confluence is generally considered secure, and reliable for application security, with robust application security measures in place. However, like any software, it is not immune to defects, especially zero-day exploits that are often targeted by nation-state actors.
What is the Latest Vulnerability in Confluence?
This is a critical issue that allows the unauthorized creation of administrator accounts in publicly accessible Confluence instances.
How widespread is this vulnerability CVE-2023-21715?
Shodan currently displays more than 1000 systems across organizations mostly in the USA let’s explore more details on the critical issue
For this critical CVE
- CVE- 10/9.8
- CTI – 1.1 (low)
- EPSS – Very High – 0.935270000
- Exploit – Confirmed
- Actors – Nation-state
- Type: Privilege Escalation
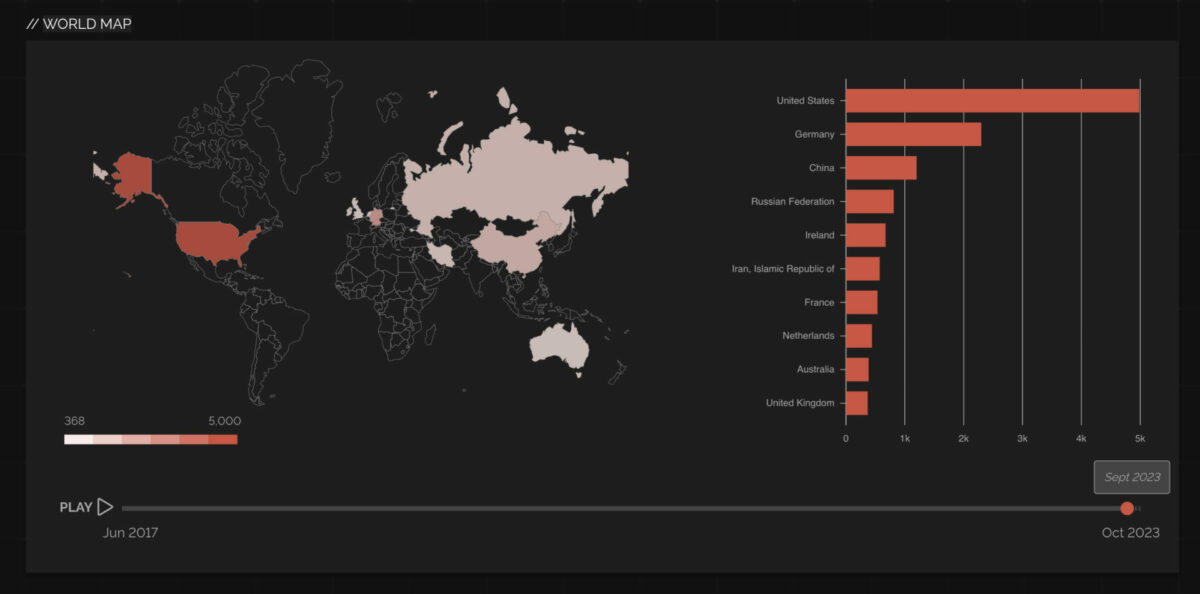
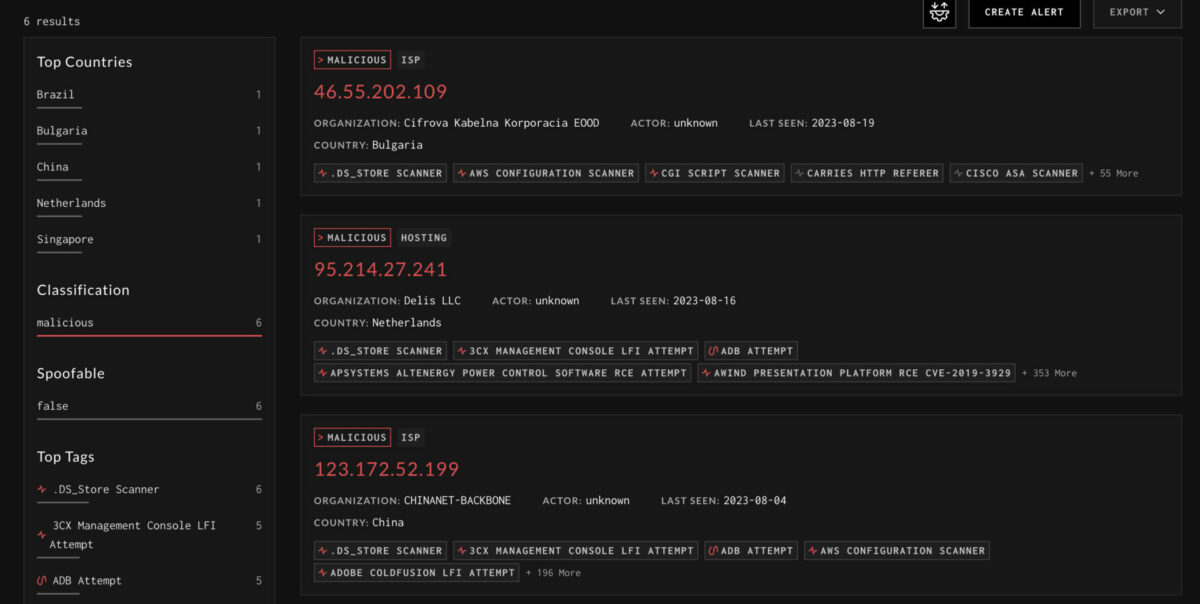
Currently, there are two streams of attackers on Graynoise divided into a group of 5 and 6 malicious actors but the growing

What are the Vulnerable Versions of Confluence for CVE-2023-21715?
CVE-2023-22515 affects Confluence Data Center and Server versions 8.0.0 to 8.5.1. It’s crucial to upgrade to the latest versions to mitigate risks.
Affected Versions CVE-2023-21715
The Confluence Data Center and Server versions listed below are affected by this vulnerability. Customers using these versions should upgrade your instance as soon as possible.
Versions prior to 8.0.0 are not affected by this issue.
| Product | Affected Versions |
|---|---|
| Confluence Data Center and Confluence Server | 8.0.08.0.18.0.28.0.38.0.48.1.08.1.18.1.38.1.48.2.08.2.18.2.28.2.38.3.08.3.18.3.28.4.08.4.18.4.28.5.08.5.1 |
Fixed Versions CVE-2023-21715
Atlassian recommends that you upgrade each of your affected installations to one of the listed fixed versions (or any later version) below.
| Product | Fixed Versions |
|---|---|
| Confluence Data Center and Confluence Server | 8.3.3 or later8.4.3 or later8.5.2 (Long Term Support release) or later |
Mitigations
One of the mitigations below will prove effective.
- Restrict external network access to the vulnerable instance
- Bring the vulnerable instance offline
- 1. Block access to the /setup/* endpoints on Confluence instances. This is possible at the network layer or by making the following changes to Confluence configuration files.On each node, modify /<confluence-install-dir>/confluence/WEB-INF/web.xml and add the following block of code (just before the </web-app> tag at the end of the file):
<security-constraint>
<web-resource-collection>
<url-pattern>/setup/*</url-pattern>
<http-method-omission>*</http-method-omission>
</web-resource-collection>
<auth-constraint />
</security-constraint>
2. Restart Confluence.
How can Phoenix security help with CVE-2023-22515
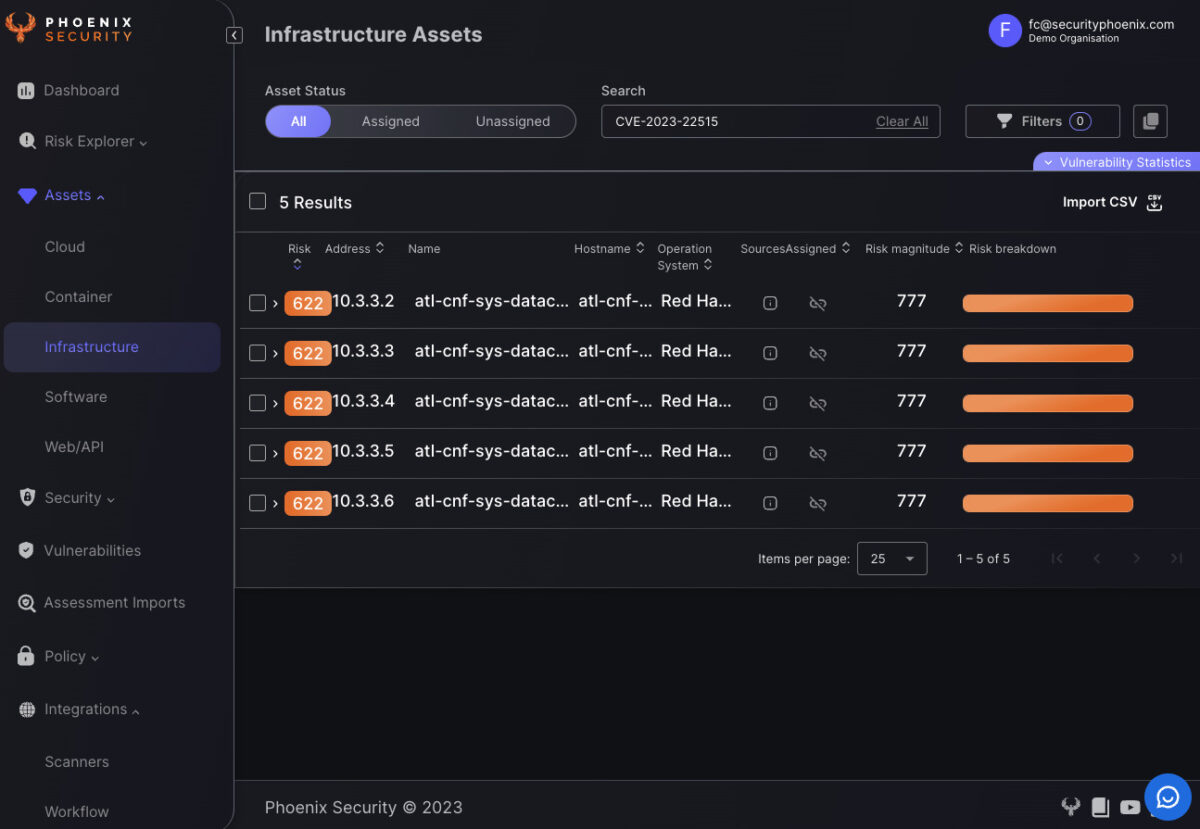
When it comes to identifying which of your systems are exposed to critical vulnerabilities like CVE-2023-22515, Phoenix Security offers a single query and pane of glass for all the risky assets.
Analyse the vulnerability in the phoenix security vulnerability screen and Infrastructure screen to identify which system has been compromised (note since the time of publishing the image the EPSS has changed)
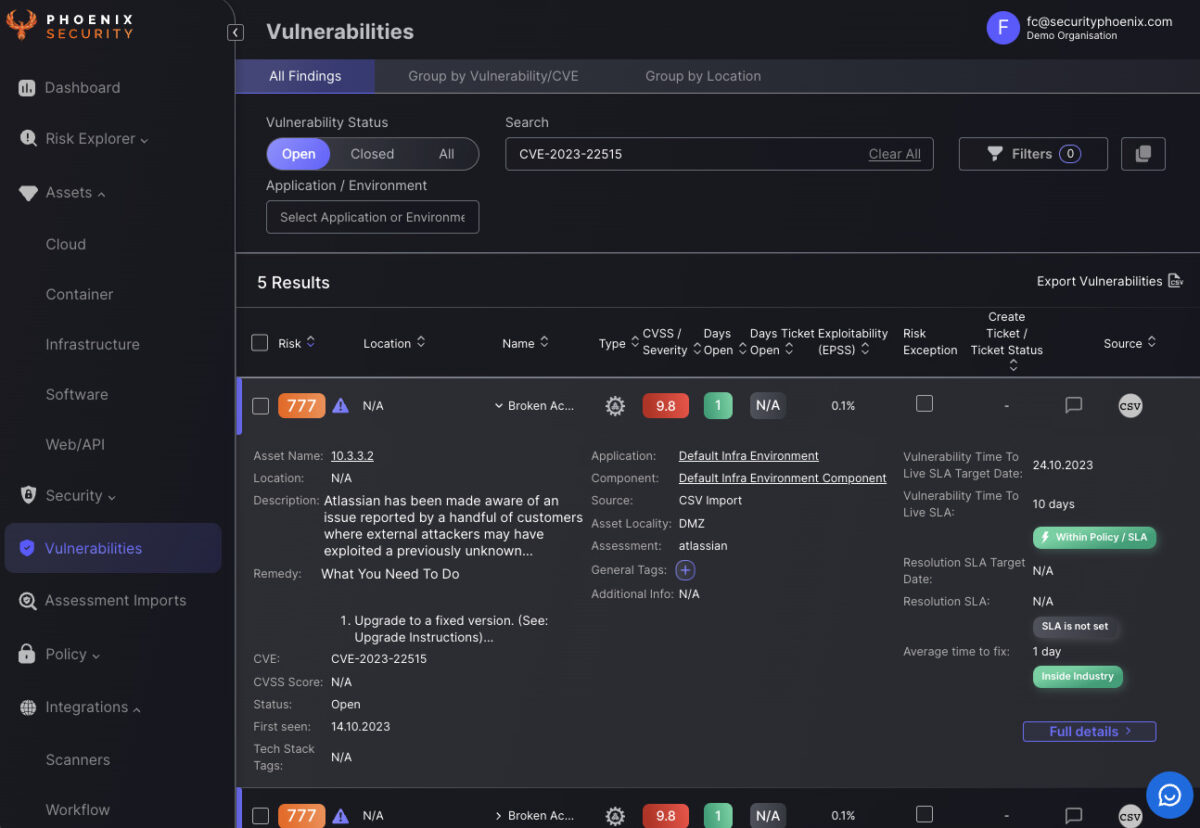
Our advanced vulnerability and infrastructure screens are designed to quickly identify systems that are externally facing, making it easier for you to take immediate action. By analyzing the CVE-2023-22515 vulnerability in both the vulnerability and infrastructure screens, Phoenix Security provides a comprehensive view of your risk landscape. This enables you to prioritize patches and other security measures effectively, ensuring that your Atlassian Confluence instances remain secure against zero-day exploits and nation-state threats.
Previous Issues of Vulnerability Weekly
- How to update curl and libcurl without panic fixing
- Critical Vulnerabilities in Atlassian Confluence: Zero-Day
- Detect & Mitigate HTTP/2: Rapid Reset Vulnerabilities
- Understanding the libcue Vulnerability CVE-2023
- Understanding and fixing Curl and libcurl
- CVE-2023-3519 Update on Critical RCE in Netscaler ADC (Citrix ADC) and Netscaler Gateway (Citrix Gateway) details on vulnerability timeline and compromise
- MOVEit Transfer breach, Zellis compromise CVE-2023-34362