
Weekly review of the top vulnerability issues of the week
This week we deep dive into Github Leak, F5 Botnet, VMWare, Windows and Linux Vulnerabilities Most vulnerabilities are being explored after the recent discoveries
Appsec
Github

In Mid April Github was attacked and the attacker leveraged the stolen Oauth app tokens issued to heroku and trvis-CI to steal 100000 NPM account Credentials
Github alerted on the 15 April of the attack and has updated the security Blog
We covered the issue in past releases Security Vulnerability of the Week 02/05/22 (updated) and https://phoenix.security/security-vulnerability-of-the-week-09-05-22/
The original List of token being stolen belonged to the following
- Heroku Dashboard (ID: 145909)
- Heroku Dashboard (ID: 628778)
- Heroku Dashboard – Preview (ID: 313468)
- Heroku Dashboard – Classic (ID: 363831)
- Travis CI (ID: 9216)
All the vendors after the breach was disclosed forced re-auth and revoked all the OAuth Tokens (GitHub, Travis CI, and Heroku) to block further hacking attempts.
Greg Ose, Senior Director for Product Security Engineering at GitHub disclosed on the 27 May the details of the ongoing investigation after an unknown threat actors stole the following data from npm cloud storage:
- Approximately 100k npm usernames, password hashes, and email addresses from a 2015 archive of user information.
- All private package manifests and metadata as of April 7, 2021.
- Names and the semVer of published versions of all private packages as of April 10, 2022.
- Private packages from two organizations.
Nonetheless recently GitHub has forced 3rd parties and all users to enable 2Factor Authentication (MFA, 2FA)
Attempting to leverage the stolen npm credentials would be automatically blocked by email verification enabled on all accounts since March 1, 2022, if they were not enrolled in 2FA already.
GitHub has reset all passwords belonging to impacted npm users and notifies all organizations and users whose data was accessed by the attacker.
“Following an internal discovery and additional investigation unrelated to the OAuth token attack, GitHub discovered a number of plaintext user credentials for the npm registry that were captured in internal logs following the integration of npm into GitHub logging systems,” Ose added.
“This issue was mitigated and logs containing the plaintext credentials were purged prior to the attack on npm.”
For more details check the message from the Hackernews forum: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=31526649
also refer to the blog from Greg Ose to follow the disclosure: https://github.blog/2022-05-26-npm-security-update-oauth-tokens/
INFRA/Network
Windows

Windows and Microsoft Active Directory, ad is strengthening Active Directory is strengthening the posture for account after recent Discoveries of Security team on Azure.
Microsoft introduced in October 2019 the “security defaults” as a mechanism designed to introduce good identity security hygiene with a minimum of effort, even for organizations that don’t have an IT team in Jan 20202. Few months later security defaults were enabled across 60K tenants.
When an administrator setups Security Defaults for tenants the users are asked to enroll for MFA within 14 days
The new security defaults will help protect enterprise user accounts from password spray and phishing attacks by:
- Requiring all users and admins to register for MFA using the Microsoft Authenticator app.
- Challenging users with MFA, mostly when they show up on a new device or app, but more often for critical roles and tasks.
- Disabling authentication from legacy authentication clients that can’t do MFA.
- Protecting admins by requiring extra authentication every time they sign in.
Linux

There has been increased attention to Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL); the system was built, as the name mentions to run on windows Linux application that emulates Linux kernel.
Malicious Linux binaries for WSL were first discovered over a year ago, with researchers at Lumen Technologies’ Black Lotus Labs publishing a report on this new type of threat in September 2021.
A more recent attack leveraging the C&C via telegram: RAT-via-Telegram Bot that allows control over Telegram
Black Lotus Labs warned in the past that threat actors are exploring the WSL vector deeper, even if many of the samples analyzed “did not yet appear to be fully functional due to the use of internal or non-routable IPs.”
The general recommendation for defending against WSL-based threats is to keep a close eye on the system activity (e.g. SysMon) to determine suspicious activity and investigate commands.
Source: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/
Vmware

New PoC Available for Vmware products to exploit the Authentication Bypass
VMware released security updates to address the CVE-2022-22972 flaw affecting Workspace ONE Access, VMware Identity Manager (vIDM), or vRealize Automation.
The flaw (tracked as CVE-2022-22972) was reported by Bruno López of Innotec Security, who found that it impacts Workspace ONE Access, VMware Identity Manager (vIDM), and vRealize Automation.
Researchers at Horizon3 released a PoC to exploit the vulnerability: proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2022-22972
Note VMware has released a cumulative patch, that addresses more than 28 new vulnerabilities
CVE-2022-22972 is a relatively simple ‘Host’ header manipulation vulnerability. Motivated attackers would not have a hard time developing an exploit for this vulnerability,” Horizon3 added.
“This script can be used by bypassing authentication on vRealize Automation 7.6 using CVE-2022-22972,” the researchers said.
“Workspace ONE and vIDM have different authentication endpoints, but the crux of the vulnerability remains the same.
The complete list of VMware products impacted by these security bugs includes:
- VMware Workspace ONE Access (Access)
- VMware Identity Manager (vIDM)
- VMware vRealize Automation (vRA)
- VMware Cloud Foundation
- vRealize Suite Lifecycle Manager
The company goes deeper into the vulnerability in their advisory: “A malicious actor with network access to the UI may be able to obtain administrative access without the need to authenticate,”
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) further highlighted this security flaw’s severity level by issuing a new Emergency Directive that ordered Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies to urgently update or remove VMware products from their networks.
patch available:
for this version: https://www.vmware.com/security/advisories/VMSA-2022-0014.html detailed under: https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/88438
Workaround:
VMware also provides temporary workarounds for admins who cannot patch their appliances immediately.
The steps detailed here – only one admin should remain, all users should be disabled and log in via SSH to restart the horizon-workspace service.
VMware and F5 weaponization

Vmware and F5 were recently the main highlights on vulnerabilities (covered in https://phoenix.security/security-vulnerability-of-the-week-09-05-22/ and in VmWare advisory: https://www.vmware.com/security/advisories.html )
The botnet recently discovered in March by Securonix originally exploited Fortinet vulnerabilities with the intent of causing Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
An update from AT&T Alien Labs notes that the latest variants of EnemyBot incorporate exploits for 24 vulnerabilities
In April most of the flaws related to routers and IoT devices, with CVE-2022-27226 (iRZ) and CVE-2022-25075 (TOTOLINK) and Log4Shell being added
The new Variant adds the following attacks:
- CVE-2022-22954: Critical (CVSS: 9.8) remote code execution flaw impacting VMware Workspace ONE Access and VMware Identity Manager. PoC (proof of concept) exploit on April 22: https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/166935/VMware-Workspace-ONE-Access-Template-Injection-Command-Execution.html
- CVE-2022-22947: Remote code execution flaw in Spring, and massively targeted in April with code: https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/166219/Spring-Cloud-Gateway-3.1.0-Remote-Code-Execution.html
- CVE-2022-1388: Critical (CVSS: 9.8) remote code execution flaw F5 big IP, threatening vulnerable endpoints with device takeover. The exploit was active almost immediately Code: https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/167007/F5-BIG-IP-Remote-Code-Execution.html
The group Keksec, behind EnemyBot, is actively developing the malware and has other malicious projects under its belt: Tsunami, Gafgyt, DarkHTTP, DarkIRC, and Necro.
Recommendation:
As always update the system externally facing as soon as possible as the exploits get weaponized quite quickly and systematically exploited with the objective of DDoS and Ransomware
Cloud
Current Year Research on Vulnerabilities Discovered
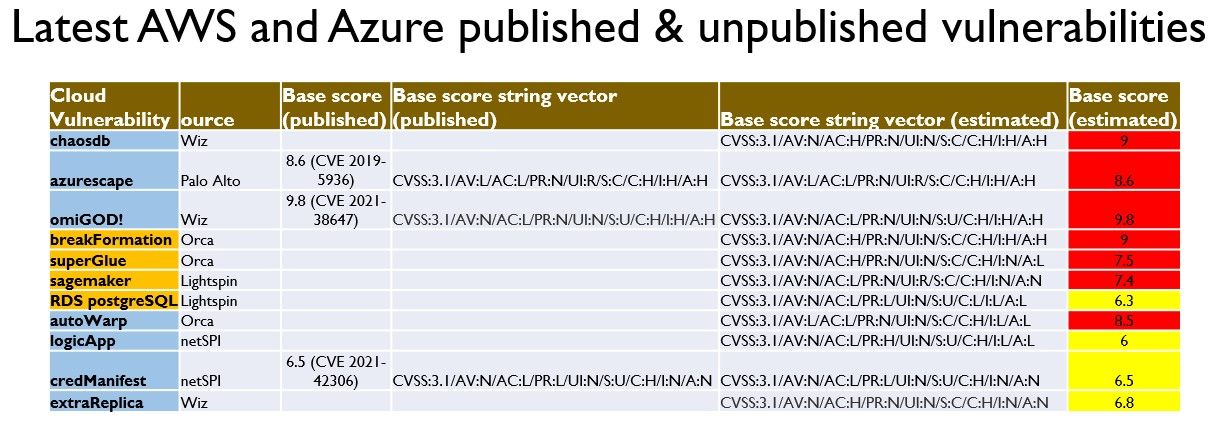
For the Deep dive on previous Cloud Vulnerabilities: https://phoenix.security/security-vulnerability-of-the-week-02-04-22/
Here https://phoenix.security/security-vulnerability-of-the-week-09-05-22/
and here https://phoenix.security/security-vulnerability-of-the-week-16-05-22/














