Prioritising vulnerabilities for application security and cloud security is becoming more and more the norm, and risk-based vulnerability prioritization is being debated in the industry against some new innovative approaches utilizing decision trees. With critical vulnerabilities being exploited in 3-15 days and business security teams being continuously overstretched, it is more important than ever to be efficient and effective in what to fix.

In recent research, only a small number of CVEs were exploitable (10-15%), and the number of vulnerabilities reported yearly is increasing 35% annually.
Although the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) has served as the base method for vulnerability fixes for years, it is important to remember that CVSS measures severity, not risk. A risk-based approach enables product security and engineering teams to make more focused decisions, communicate efficiently with the rest of the organization, and prioritize vulnerabilities based on location, the likelihood of exploitation, and business impact.
Nonetheless, CVSS can be referred to as severity, not risk. A risk-based approach (details can be seen in security risk formula) on vulnerabilities from code to cloud-enable product security and engineering team to:
- Make more focused decisions
- Communicate efficiently with the rest of the organization on risk
- Prioritise vulnerabilities based on location, the likelihood of exploitation and business impact
What is risk
Risk can be described as the potential impact on business operations or assets and the likelihood of exploitation. In cybersecurity, risk assessment helps organizations determine which vulnerabilities pose the greatest threat and should be addressed first.
What is risk-based vulnerability prioritization?
“ Security and risk leaders should tie vulnerability management practices to their organization’s specific needs, not a mythical standard.” Gartner
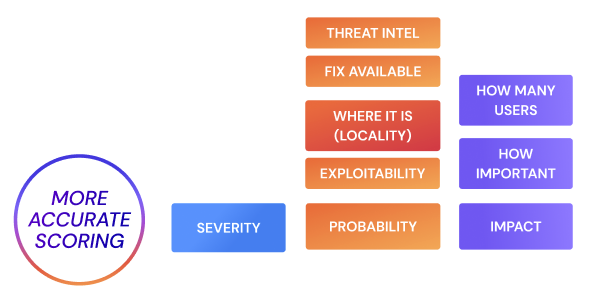
Risk specified in this way is extensible and allows to include in Probability, impact and severity several factors that can then be scaled and expanded, offering a consistent and quantifiable unbiased view across the entire organization.
Those methodologies can be applied fro software and application security as well as infrastructure security and cloud security.
The above risk levels can also be scaled easily with aggregation into several layers and form the risk for application, environment, business units and so on, making it a prime tool for
Detailed specifications on risk formula is available at security risk formula
As long as the organization keep a transparent approach to how the elements of the risk are being calculated
What are decision trees?
Decision trees are a graphical representation of various decisions and their corresponding outcomes. They help security teams visualize and evaluate complex decision-making processes by breaking them down into smaller, manageable steps.
Following an Example of decision trees for Business impact analysis vulnerability prioritization
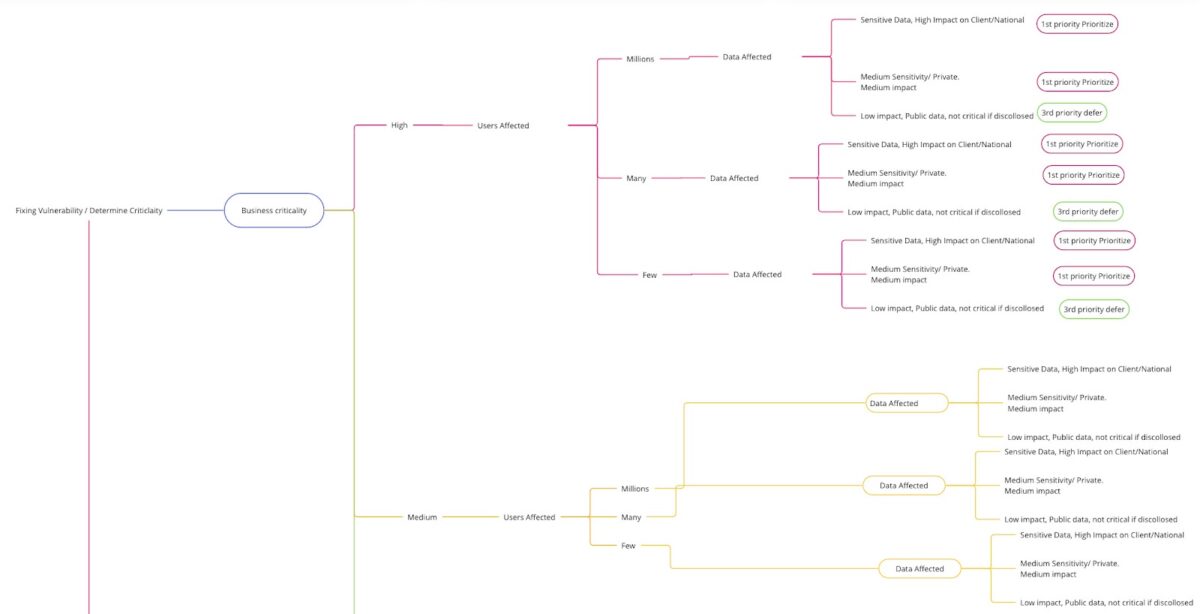
Following another example of decision trees for vulnerability prioritisation (arrow pointing from the previous diagram)

SSVC from cisa

The SSVC (System and Services Visibility and Control) program is a cybersecurity initiative developed by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to help organizations improve their cybersecurity posture by increasing visibility into their systems and networks, and enabling better control over them. For more details refer to the Detailed guidance.
The SSVC program aims to provide organizations with guidelines and best practices for implementing security controls that help them detect and respond to cyber threats more effectively. These controls are organized into system and communications protection, access control, and incident response.
To use the SSVC program, organizations can refer to the SSVC guide that was mentioned earlier. The guide provides detailed descriptions of the security controls recommended for each category and guidance on implementing and maintaining them. Organizations can use this information to assess their security posture, identify areas where they need to improve and implement the recommended controls to protect their systems and data better.
When implementing the SSVC controls, organizations should consider several decision parameters, such as the level of risk they are willing to accept, the cost and complexity of implementing the controls, and the impact they may have on their operations. For example, organizations may choose to implement more stringent controls in high-risk areas, such as systems that store sensitive data or control critical infrastructure, while implementing more relaxed controls in lower-risk areas.
The CISA SSVC program provides organizations a useful framework for improving their cybersecurity posture and protecting their systems and data from cyber threats. By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in the SSVC guide, organizations can reduce the risk of cyber-attacks and increase their overall resilience to cyber threats.
Other considerations of decision trees can be found here
Advantages and disadvantages
By understanding the advantages and drawbacks of each method, organizations can make an informed decision on which approach best suits their needs for prioritizing vulnerabilities and enhancing their cybersecurity posture.
As a product security and vulnerability management team, you want to be consistent but collaborative.
A method that relies on strict rules is bound to fail as enterprise organizations and decision-making are wild and change consistently.
Nonetheless, a too-loose or undocumented method might result in chaos and wildly different decision methods.
A combination of risk-based decisions and decision trees based on risk factors is the optimal method as it relies on an objective view of the risk plus a decision method that allows flexibility and exceptions.
| Decision Trees | Risk-Based | Mixed Risk-based and Decision three | |
| Pro | Simple to explain, facilitating communication among team members. Consistent, ensuring uniformity in the decision-making process. | Accounts for probability, offering a more comprehensive assessment of risk.Allows for adjustment of weights for various factors, providing flexibility in the evaluation process. Transparent decisions can be overridden, enabling organizations to adapt to change circumstances. Supports linear logic (accept/record/defer), streamlining decision-making. | Combines the strengths of both Decision Trees and Risk-Based Scoringoffering a more holistic approach. Transparent decisions can be overridden, ensuring flexibility in decision-making. Supports linear logic (accept/record/defer), optimizing the decision process. |
| Con | It does not account for probability, potentially overlooking important risk factors. Difficult to scale, as the complexity increases with more decisions and outcomes. Binary decisions limit the scope of possible outcomes. Subjective to the creator, which can introduce bias or subjectivity. | Decisions not always binary, complicating the process in certain situations.Requires a formula, which may be challenging for some team members to understand. | Requires a more advanced maturity level, which may be challenging for some organizations to achieve. Business criticality and other elements can be difficult to determine, necessitating specific methods to specify. It can be hard to explain, requiring justification and trust in the model. Some factors are hidden in the calculation, necessitating verification and trust in the model. |
Additional considerations
When comparing decision trees and risk-based prioritization, it is essential to consider the strengths and weaknesses of each approach. The table below outlines the key differences between these two methods:
| Criteria | Decision Tree | Risk-based Prioritization |
| Visualisation | Provides visualisation of decisions | Can lack graphical decision representation |
| Complexity | Simplifies complex decisions | Can handle complex situations |
| Collaboration | Encourage team collaboration | It may require more communication on risk and detailed visualisation on what are the factors influencing risk |
| Scope | Limited to predefined scenarios | More adaptable to various situations and extendible |
| Precision | May oversimplify decisions | Consider a wide range of factors, easy to extend and scale |
| Subjectivity | Subject to the creator’s expertise and bias | Relies on objective risk assessment and data |
| Weights | Does not support weight in decision making | Supports weight in deciding what to fix and which parameter to weigh |
Conclusion
In summary, decision trees offer a simplified, visual approach to decision-making that encourages collaboration but may be limited in scope and susceptible to subjectivity. On the other hand, risk-based prioritization enables organizations to assess vulnerabilities based on a wider range of factors and adapt to various situations. However, it may lack the graphical representation that decision trees provide and may require additional communication effort within the team. Ultimately, organizations should weigh the pros and cons of each method and determine which approach best fits their specific needs and circumstances.
Using decision trees and risk-based prioritization enables product security teams to:
- Communicate consistently and effectively about platform risk across the organization.
- Address vulnerabilities efficiently and effectively.
- Make informed decisions on vulnerability prioritization.
How Phoenix Security Can Help:
Phoenix Security is a platform that collects information from various sources, contextualizes, and prioritizes vulnerabilities from code to cloud.
If you want to know more about Phoenix security and doing vulnerability management at scale, contact us https://phoenix.security/request-a-demo/
Get in control of your Application Security posture and Vulnerability management
Phoenix risk calculation enables automatic prioritization of vulnerabilities using multiple data points and assessing quickly based on context, providing box Cyber threat intelligence. All data points from phoenix security are transparently shown to enable risk-based prioritization. Phoenix security risk provides decision data points and risk-scoring methods, enabling organizations to make informed decisions regarding their cybersecurity strategy. By leveraging Phoenix Security’s comprehensive platform, organizations can streamline their vulnerability management and better protect their digital assets.