- 27th April 2025
The journey of securing an organization’s application landscape varies dramatically, depending on where a company stands in its maturity. Early-stage startups with small security teams face challenges not only with vulnerabilities but also with scaling their security processes in line with their growth. On the flip side, established enterprises struggle with managing complex environments, prioritizing remediation, and dealing with vast amounts of vulnerabilities while staying ahead of sophisticated threats.
For startups, the focus is clear—establish visibility and ensure core security practices are in place. Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) tools provide a straightforward, automated approach to detecting vulnerabilities and enforcing policies. These solutions help reduce risk quickly without overburdening small security teams.
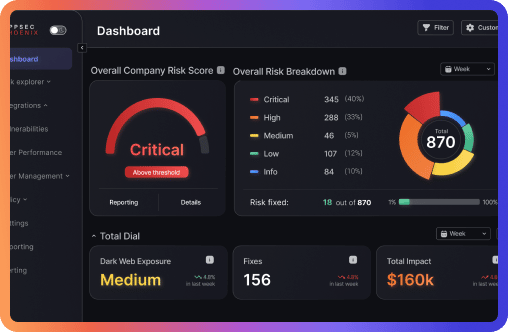
Mature organizations, on the other hand, are tackling a different set of problems. With the sheer number of vulnerabilities and an increasingly complicated threat landscape, enterprises need to fine-tune their approach. The goal shifts toward intelligent remediation, leveraging real-time threat intelligence and advanced risk prioritization. ASPM tools at this stage do more than just detect vulnerabilities—they provide context, enable proactive decision-making, and streamline the entire remediation process.
The emergence of AI-assisted code generation has further complicated security in both environments. These tools, while speeding up development, are often responsible for introducing new vulnerabilities into applications at a faster pace than traditional methods. The challenge is clear: AI-generated code can hide flaws that are difficult to catch in the rush of innovation. Both startups and enterprises need to adjust their security posture to account for these new risks. ASPM platforms, like Phoenix Security, provide automated scanning of code before it hits production, ensuring that flaws don’t make it past the first line of defense.
Meanwhile, organizations are also grappling with the backlog crisis in the National Vulnerability Database (NVD). A staggering number of CVEs remain unprocessed, leaving many businesses with limited data on which to base their patching decisions. While these delays leave companies vulnerable, Phoenix Security steps in by cross-referencing CVE data with known exploits and live threat intelligence, helping organizations stay ahead despite the lag in official vulnerability reporting.
Whether just starting their security program or managing a complex infrastructure, organizations need a toolset that adapts with them. Phoenix Security enables businesses of any size to prioritize vulnerabilities based on actual risk, not just theoretical impact, helping security teams navigate the evolving threat landscape with speed and accuracy.
Francesco Cipollone