
Product Security the pillars of the programme – Vulnerabilities and Measurements
Numerous conversations inspired this blog over the new series of podcasts (www.cybercloudpodcast.com) we are about to publish
The challenge with product security is a priority, lighting the immense stream of issues coming to various teams from various domains and making them a priority (for the team and the business).
One particular quote I liked is that not all problems are equally important or worth solving.
In my past life as product security, the elements that I found key were:
- Socialising the problem
- Translating the problem in business terms
- Getting buy-in from business overall
- Measuring everything (new assets, new vulnerabilities)
- Contextualising and enriching as much as possible with metadata from platforms like Github, AWS, azure etc…
- Prioritising using elements available and threat intelligence (there are a lot of APIs for threat intelligence out there at a reasonable price)
Another element that struck me is the level of burnout and overall doom and gloom linked to starting a programme of work like application security, vulnerability management or product security.
Product Security Pillars with a focus on Vulnerability Management
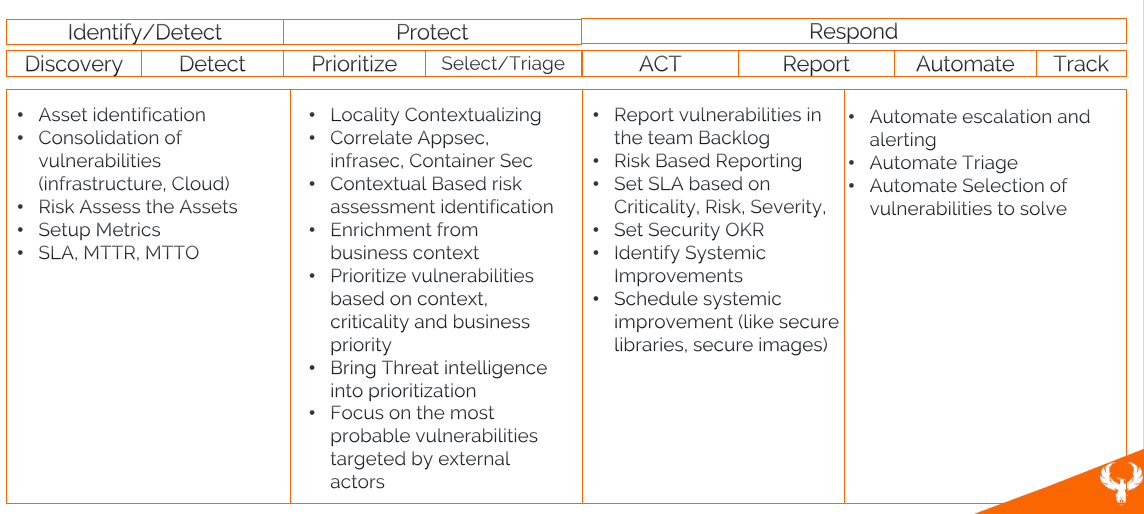
So what needs to be done in the programme?
First of all, let’s start with NIST as a guideline as well as the number of actions:
- DISCOVERY Asset management and the identification of problems and where they are
- PRIORITISE Acting on the problems and prioritising based on threat intel, locality (where the assets are deployed) and threat intelligence related to those assets
- PRIORITISE: Correlate and contextualise application security, infrastructure security
- SELECT & TRIAGE automatically vulnerabilities based on how important they are and where they are
- ACT/REPORT: Reporting the vulnerabilities to the right teams
- ACT/REPORT: Automating the mitigation and triage of vulnerabilities
- ACT on the vulnerabilities by solving them week on week and sprint on sprint,
- TRACK: measure the progress toward resolution and metrics established
Vulnerability Management Maturity Evolution Framework
What should you do from the getgo? Implement the whole platform and metrics. Yes, if you have infinite time and resources…but unfortunately, nowadays we don’t have those leasure so, to address those challenges, we have proposed a phased approach (upcoming blogs and https://phoenix.security/data-driven-vulnerability-managementre-sla-slo-dead/ will cover this maturity model extensively)
What metric shall be used in this programme? You can find a number of another articles
- vulnerabilities and SLA https://phoenix.security/vulnerability-sla-slo-okr-in-application-cloud-infra/
- We also analysed some metrics like SLA MTTO and other metrics: https://phoenix.security/vulnerability-infrastructure-and-application-security-sla-slo-okr-do-they-matter/
- Upcoming whitepaper: https://phoenix.security/data-driven-vulnerability-managementre-sla-slo-dead/
Challenges and Workflows for Modern Vulnerability managment
Why is it challenging to correlate all those elements together? Those activities tend to be seen in different siloes while they are a chain of relationships between various elements deployed in a modern stack. The elements described above are a sequence of logic that traditionally is manually assessed by teams
1 – Contextualize and aggregate issues from multiple perspectives
- Software and libraries
- Cloud misconfigurations and cloud issues
- Container Misconfiguration
- Infrastructure Vulnerabilities, O/S, Devices etc..…
2 – Correlates, Contextualize, Prioritize
- Aggregate vulnerabilities from the source above and remove duplicate and ephemeral assets.
- Contextualise vulnerabilities based on Locality
- Contextualise and enrich vulnerabilities based on Business Metadata (Criticality, Data Accessed)
- Risk assess vulnerabilities
- Prioritise vulnerabilities based on risk and all the elements described above
- Criticality of vulnerability
- Probability of exploiting vulnerabilities from the locality (internal, external, data access…)
- Probability of exploiting vulnerabilities based on external monitored factors (CVS exploitation in the wild, EPSS Data, CISA Prioritization)
- Probability of exploitation based on likelihood: speed of resolution of vulnerability from other companies in the same industry
- Probability of exploitation based on Cyber Threat Intelligence: monitoring threat intelligence and who is targeting you, your industry, and specific CVE
- Probability of exploitation based on Cyber Threat Intelligence: monitoring mention of vulnerabilities and sentiment analysis on clear web and dark web
In conclusion
The steps to implement a cybersecurity programme around application security, cloud, and infrastructure security with vulnerability management at its core is not easy but are doable.
The key pillar is buy-in from the organization, starting small and demonstrating progress. Starting with a scope that is too wide or several activities that are too complex results in a light demonstration of traction.
Measurement and early data help demonstrate success; volumetrics, MTTR, MTTO, and similar can be key to risk reduction. Some tools can enable you to monitor some of those metrics; Phoenix Security can help you track vulnerability resolution, correlate and prioritize vulnerabilities and track the path to green. Contact us to see how we can help you measure progress at every stage of the lifecycle.
Notes and thanks
A good inspiration for this blog was: https://www.anshumanbhartiya.com/posts/prodsec-roadmap

















