Vulnerability management is an important part of cybersecurity and is essential for organizations to protect their systems and data from malicious actors.
In this article, we will discuss the various strategies that organizations can use to manage their vulnerabilities effectively.
We will explore the different types of solutions available and how each one can help organizations protect their systems and data. Finally, we will discuss the importance of regularly monitoring and updating these solutions to ensure that vulnerabilities are detected and addressed quickly and efficiently.
Vulnerability Management: In a Nutshell
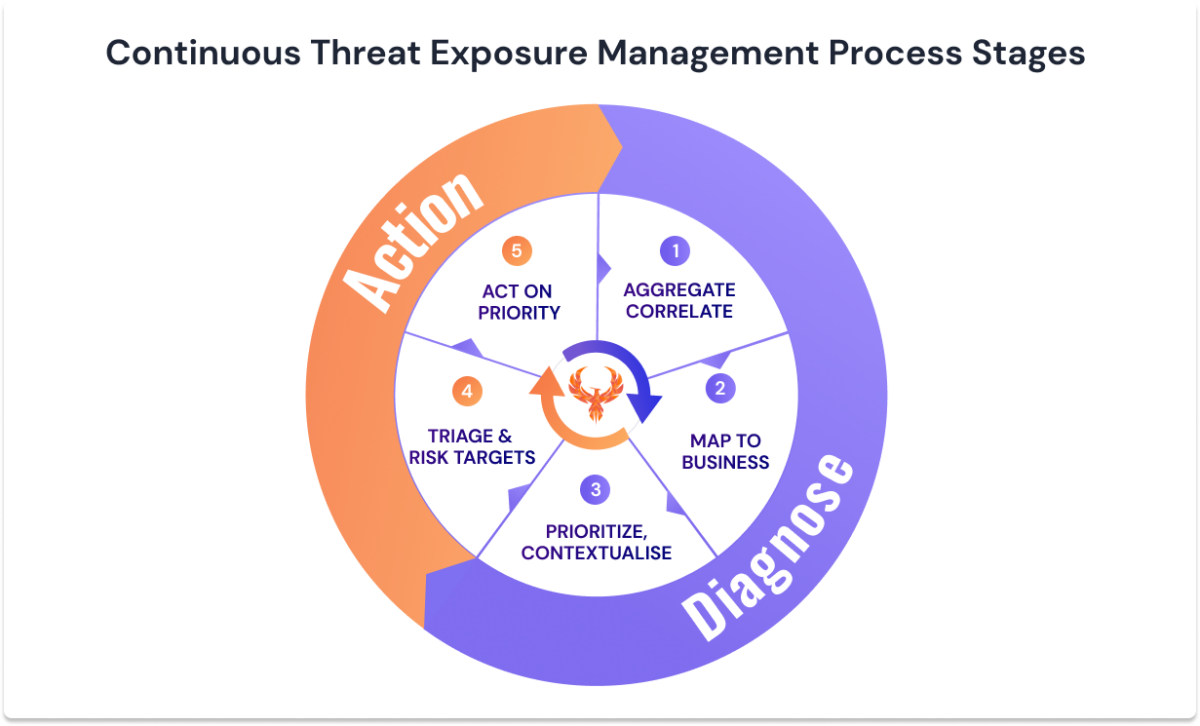
It is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating vulnerabilities. It involves a cycle of identifying, analyzing, and responding to security issues and continuous monitoring of the environment to identify new or modified risks and take appropriate action.
The goal is to reduce the overall risk to an organization’s assets and systems by preventing, detecting, and responding to threats. This includes regularly patching and updating software, implementing security controls, and enforcing security policies.
Strategies & Types — Vulnerability Management
Inventory & Asset Management
Inventory & Asset Management refers to the management of physical materials and equipment within an organization. It involves tracking and controlling the movement, use, and storage of inventory and assets. Examples include tracking raw materials, components, and finished goods inventory and tracking and managing capital equipment and other fixed assets.
It entails tracking, monitoring, and controlling inventory to ensure that the right amount of inventory is available at the right time while minimizing costs and maximizing profits. For example, an organization might track the number of units of a product in stock, the purchase price and current market value, the inventory’s physical location in a warehouse, and the number of days an item has been in stock.
Asset management involves tracking the costs of owning and operating physical assets, such as capital equipment and property. For example, an organization might track the purchase price and acquisition date of a piece of equipment, its depreciation rate, and the asset’s estimated value at the end of its useful life. Asset management also involves tracking the asset’s condition, its maintenance and repair costs, and any current or future liabilities associated with it.
Patch Management
Patch Management is detecting, downloading, testing, and deploying software patches for software applications, operating systems, and hardware components of a system. Patches are software updates or fixes released by software vendors to address security vulnerabilities, performance issues, or bug fixes.
Patch Management also involves scheduling, tracking, and reporting on the status of patches, as well as managing patch levels across a system to ensure that all patches are up-to-date. Patch Management can be a complex process involving multiple systems, users, and applications and requires a clear understanding of an organization’s network and systems.
Configuration Management
Configuration Management (CM) is a component of Vulnerability Management that helps organizations maintain control over their IT systems and assets. CM ensures that all systems are configured correctly, securely, and in compliance with organizational policies. It also helps organizations ensure that their systems are able to respond quickly and effectively to changes in their environment.
CM includes activities such as reviewing system configurations, patching and updating software, and hardening systems against attack. It helps organizations identify, address, and monitor changes to system configurations and settings. CM also helps organizations proactively reduce their risk of attack by addressing vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
In addition, CM helps organizations identify and remediate critical security issues. With CM, organizations can ensure that systems are properly configured, patched, and up-to-date. This helps protect against vulnerabilities, reduce the risk of attack, and improve overall security posture.
Network Mapping & Monitoring
Network Mapping & Monitoring in Vulnerability Management is a process of documenting and monitoring the critical networks, systems, and applications to identify potential vulnerabilities. The goal of network mapping and monitoring is to identify any security flaws that can be exploited by malicious actors, such as hackers or malware. It is a proactive process that helps organizations identify and address security issues, ultimately reducing the likelihood of an incident occurring.
Tools for Network Mapping
Organizations can use a variety of tools to map and monitor their networks, such as asset management systems, network scanners, and intrusion detection systems (IDS). Asset management systems help organizations track and organize information about the devices and services connected to the network, such as hardware and software versions, as well as patch levels.
Network scanners allow organizations to identify any open ports or services running on the network, and can be used to detect any potential vulnerabilities. An IDS monitors the network for suspicious activity and can alert administrators of any potential threats.
Vulnerability Assessment Tools
Once a network has been mapped and monitored, organizations can use vulnerability assessment tools to identify any potential vulnerabilities. Vulnerability assessment tools can be used to scan networks, applications, and systems to identify potential security issues, such as unpatched software or misconfigured settings.
After any vulnerabilities have been identified, organizations can use vulnerability management tools to address them. Vulnerability management tools can be used to patch software, modify settings, and deploy additional security measures to ensure the network is secure.
Which Vulnerability Management tool to use?
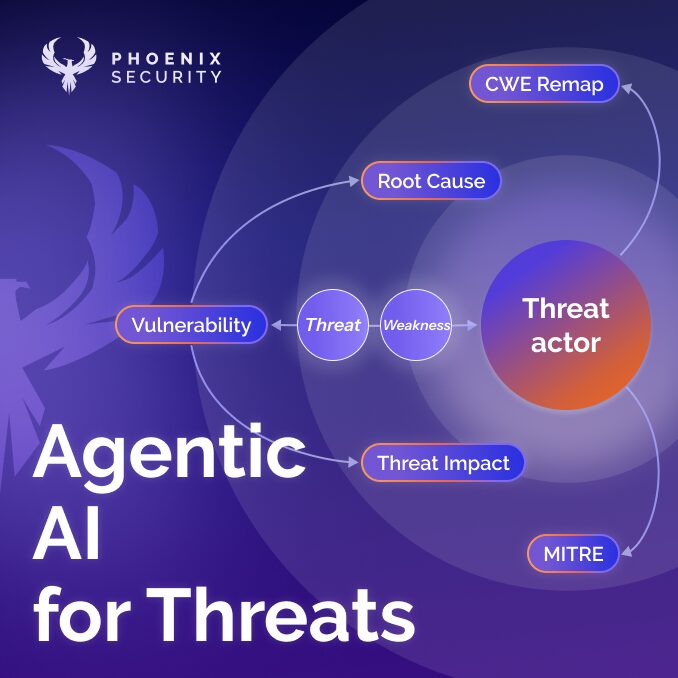
Phoenix ACT (Analyze and Contextualize Threats) is an AI-powered platform that helps organizations stay on top of their threat landscape. It uses advanced analytics and vulnerability scanning to analyze and contextualize threats, enabling organizations to become proactive in protecting their digital assets.
Using Phoenix ACT for Vulnerability Management, organizations can quickly identify, analyze and prioritize threats before they become a major issue. The tool uses predictive analytics to accurately identify vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take action before they become a major problem. It also provides risk scores to help organizations determine which threats are most critical and should be addressed first.
The platform also provides actionable insights on how to remediate critical threats. This includes tailored remediation plans that provide a clear roadmap on how to address the threats and reduce the risk of them becoming a major issue.
Bottom Line
Vulnerability management is an integral part of any secure network and should be a priority for any organization. It is essential to use the available tools and techniques for identifying vulnerabilities, mitigating their effects, and ensuring that no new vulnerabilities are introduced.
In addition to the above-mentioned measures, organizations should also establish and maintain a security policy that outlines how the vulnerabilities in the network should be managed. By taking these steps, organizations can ensure that their networks remain secure and that the assets and information they contain remain secure.