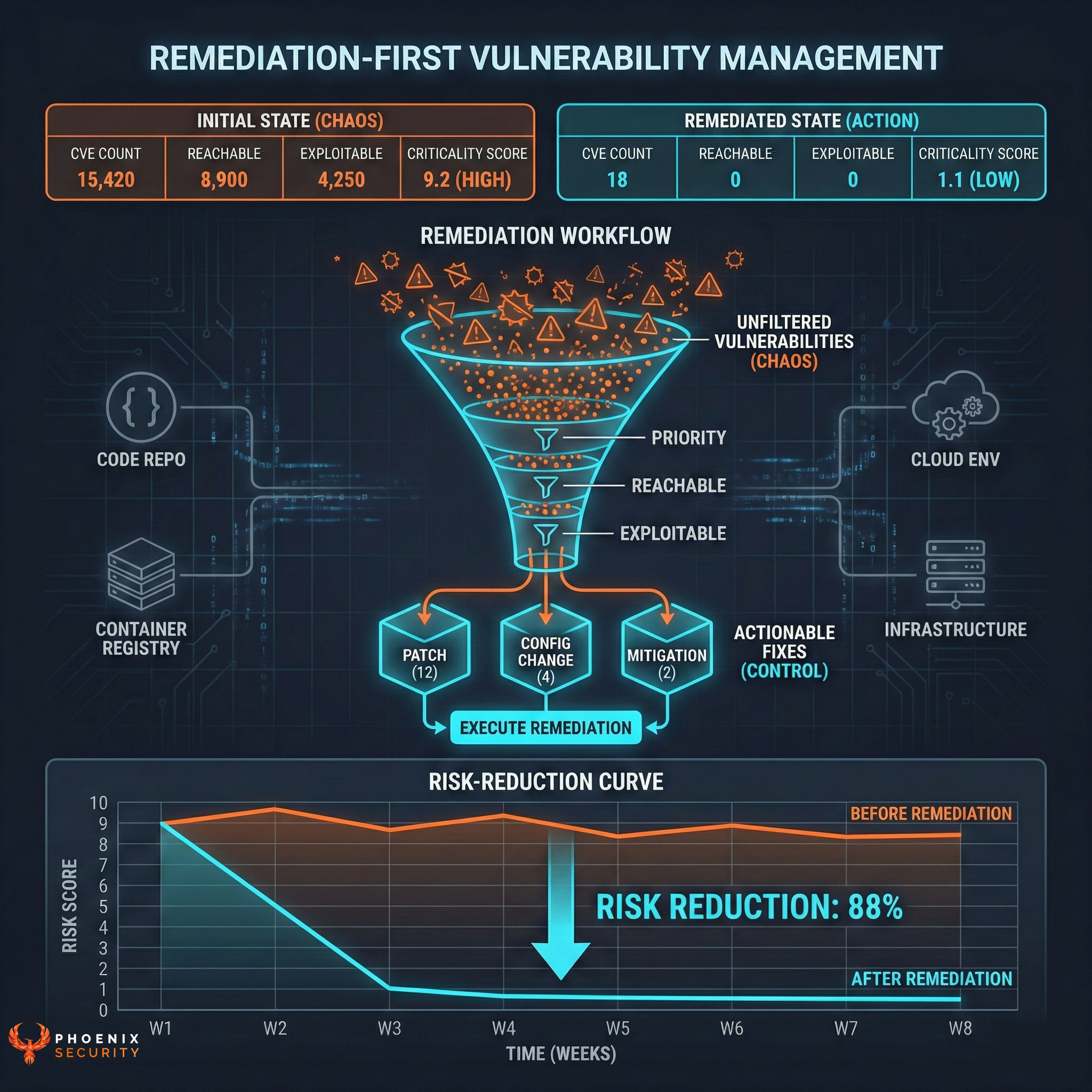
The Cloud Security and AppSec teams at Phoenix Security are pleased to bring you another set of new Phoenix Security Features and improvements for vulnerability management across application and cloud security engines. This release builds on top of previous releases with key additions and progress across multiple areas of the platform.
We are sure that you’ll find these quite interesting!
- Manage your Vulnerabilities and Assets
- Vulnerability Filtering and Sorting
- Location column in Vulnerabilities list
- Default Configuration for Context Rules
- Customisation of the number of tickets per backlog
- Productivity and User Experience
- Loading indicators and other usability improvements
- More efficient use of space in Vulns tables
- Integrations
- Tenable.io VM integration
- Unified scanner integrations page
- Outbound Vulnerability API (preview)
Manage your Vulnerabilities and Assets across application security and cloud security.
Contents
ToggleVulnerability Filtering and Sorting
Our users can now leverage the Vulnerabilities page even more. A complete set of filters and sorting options ensures they can select the exact set of vulnerabilities of interest to them. Not only that, but you can even snapshot the “filtering” URL and bookmark it or share it around!



Location column in Vulnerabilities list
When working with our Vulnerabilities screen, it might be easy to forget that we look at “findings” rather than vulnerability definitions. In other words, if we have CVE-1234-1234 affecting several “locations” (assets) in our state, we will see one entry for each since we need to address each individually. This can sometimes give the impression that there is duplicity in the platform when in reality, what we see is “detail”.
We have included a Location column in the vulnerabilities list to clarify this screen’s contents and provide additional relevant information. This column displays a recognisable name or ID for the asset or location affected by the vulnerability. And since these names can be quite long and tend to have a common prefix, we are displaying the end of the names – hopefully, this will make them easier to recognise.

Default Configuration for Context Rules
Phoenix Security’s Context Rules are a powerful way to define which assets are externally accessible. This “locality” has an impact on risk calculation and vulnerability selection.
Since there are some reasonably standard scenarios for infra assets, we have defined a set of default rules based on the type of IP address assigned to the asset: private IPs ranges are considered internal, and the rest are considered external.
These are just defaults, which users can change at any time.

Customisation of the number of tickets per backlog
Phoenix Security always could auto-create issue tickets in external systems configured by our users. We recently introduced a control to determine how many tickets should be auto-created for each external queue or project. Since the number of tickets selected to fix can vary widely depending on the selected risk target, this control offers a safety net for our users.
Now users can define what number of new tickets Phoenix should open on each project at any point in time.

Productivity and User Experience
Loading indicators and other usability improvements
We continuously seek ways to improve our users’ experience on the Phoenix platform. Providing timely feedback when the system is busy fetching or computing is an important part of that, and we are constantly adding UI elements to improve this area.
More efficient use of space in Vulns tables
Further improvements have been made to the Vulnerabilities list page, which now has more visual elements to help users quickly identify the type of vulnerability and scanner for each entry.

Integrations
Tenable.io VM integration and others

Joining our native integration with Nessus servers, we now have a direct API integration with your Tenable.io instance to fetch infrastructure (VM) vulnerabilities. Other integrations were available here.
It takes two minutes to connect to your instance and fetch vulnerabilities into the Phoenix platform. You can see our guide here: https://kb.phoenix.security/?ht_kb=integration-with-tenable-io-vm

Unified scanner integrations page
Now users can see all their scanner integrations and all those available in a single page. Creating, editing and removing scanner integrations is now easier than ever.
Outbound Vulnerability API (preview)
In tandem with the vulnerability filtering capabilities in the UI, users can now take advantage of our API to fetch the exact subset of vulnerabilities that they need. This functionality is still in review, but don’t hesitate to contact us if you want to take it for a spin.