Exploits are the translation of vulnerable code in malicious effect that can lead to security breaches. They can be particularly menacing when they involve zero-day vulnerabilities, which are previously unknown to software developers or vendors. Threat actors keenly eye these unpatched weaknesses, understanding that they are inherently difficult to defend against because there are no fixes readily available. Instead, organizations must rely on compensating controls and vigilant vulnerability management to mitigate the risks posed by zero-day exploits.
More details about exploitability can be found here in this deep dive analysis.
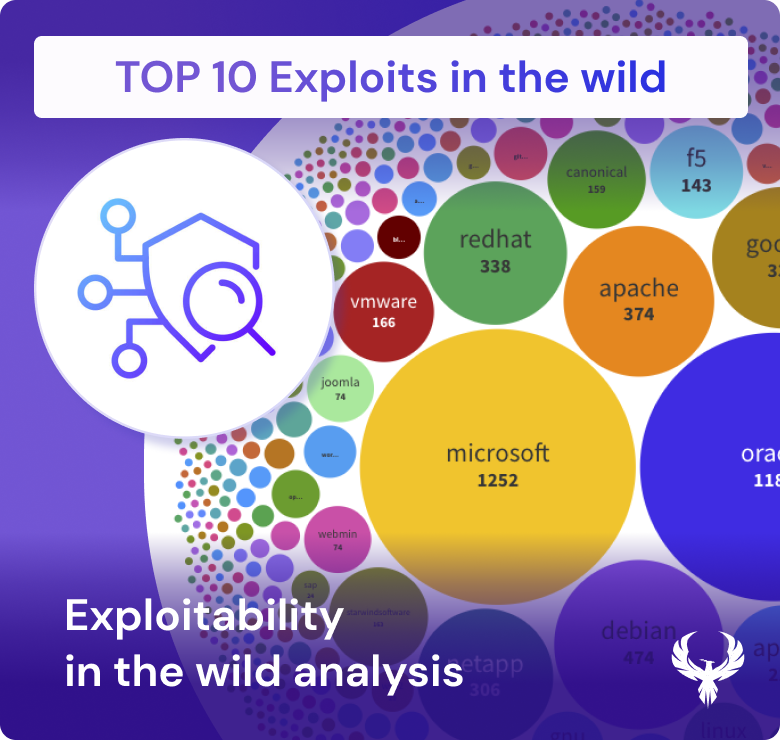
The treacherous path of exploitation begins with the discovery of a vulnerability, often documented by security researchers or attackers. Once a vulnerability is known, it doesn’t take long for links to emerge in various sources, pointing to the exploit’s existence. These exploits find their way into widely adopted vulnerability tools like ExploitDB, MetaSploit, and Nuclei, exponentially amplifying their threat potential.
The real alarm bell rings when a vulnerability achieves a high exploitation score in the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS), surpassing the threshold, perhaps 0.5 or 0.6. This score indicates that the vulnerability is not merely theoretical; it’s actively being exploited in the wild.
In this intricate landscape, understanding the dynamics of exploitability, exploits, and their relationship to vulnerability management and application security is paramount. Organizations must stay vigilant, ready to employ compensating controls and proactive security measures to defend against these cunning and ever-evolving threats.
In this section we analyse zero day data cron dark web and other sources like Zero day initiative and google zero day in the wild