Contents
ToggleQuick summary in a visual form of vulnerability management and contextualization
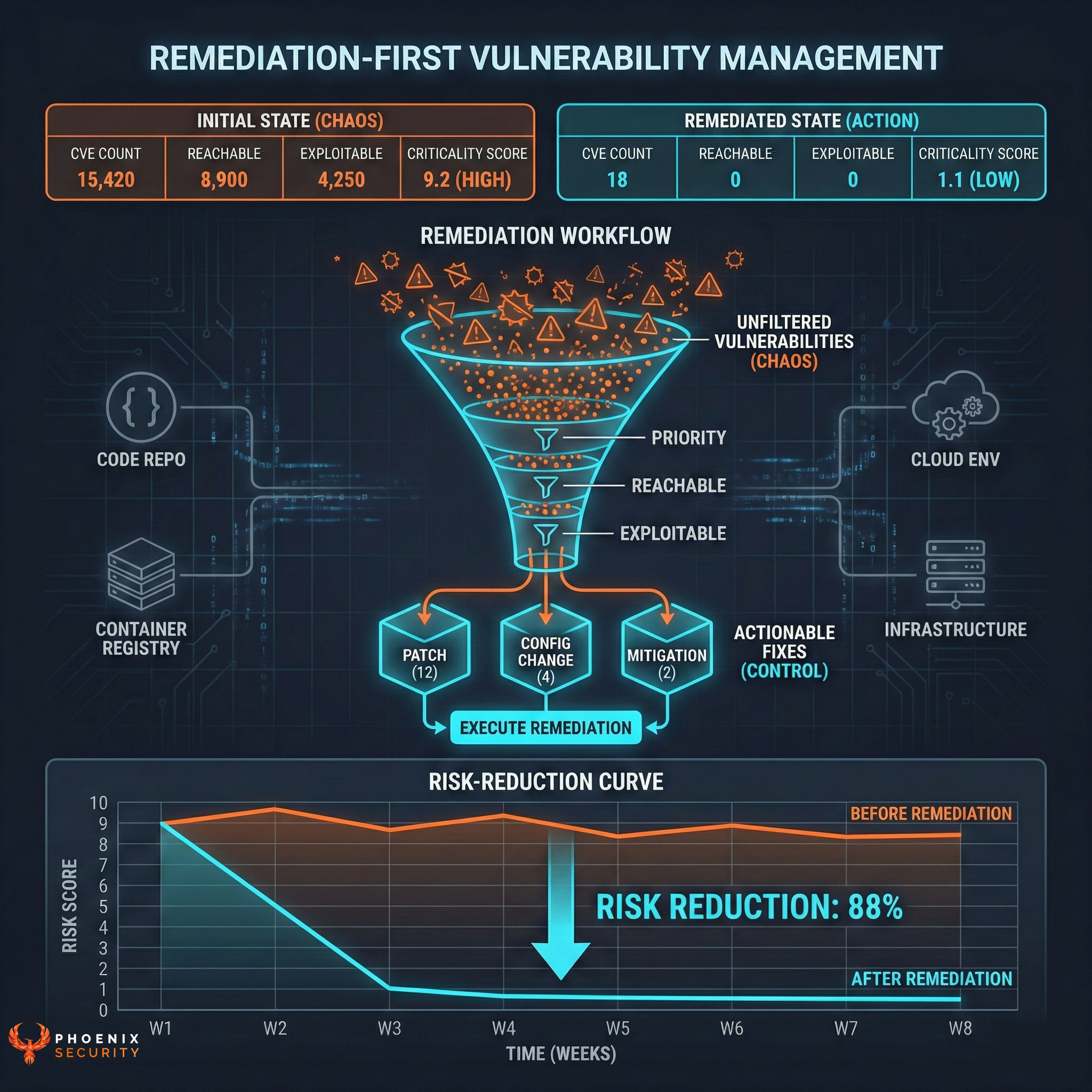
Contextual vulnerability management is a comprehensive approach to identifying, analyzing, and mitigating software and cloud infrastructure vulnerabilities. We have written extensively on the power of prioritization and contextualization. Gartner has as well recently published a number of articles on the power of risk-based vulnerability management. Contextual vulnerability management involves considering the specific context and environment in which vulnerabilities exist, including the software and hardware components, the network infrastructure, and the organizational policies and processes. By adopting this approach, organizations can more effectively assess and mitigate the risks posed by vulnerabilities, helping to protect their assets and maintain the security of their systems and networks.

Contextual vulnerability management involves identifying vulnerabilities within the context of the specific environment in which they exist. This includes understanding the relationships and connections between different systems, software, and networks and how a vulnerability might impact them.

The process of contextual vulnerability assessment involves analyzing vulnerabilities within the context of the specific environment in which they exist, including the software and hardware components, the network infrastructure, and the organizational policies and processes in place. By understanding the specific context of a vulnerability, organizations can more accurately assess its potential risks and take appropriate action to mitigate them.

Effective contextual vulnerability management requires a range of strategies and tools to protect against potential threats. This includes continuous vulnerability monitoring, patch management, threat intelligence, vulnerability analysis, and network security. By implementing these measures, organizations can better defend against vulnerabilities and maintain the security of their systems and networks.

By adopting a contextual approach to vulnerability management, organizations can more effectively assess and mitigate the risks posed by vulnerabilities, helping to protect their assets, including their data, systems, and reputation.
What is Vulnerability management, and how does contextualization play a critical role?
Vulnerability management is a critical aspect of cybersecurity and IT risk management. It involves identifying, analyzing, and mitigating systems, networks, and software vulnerabilities. While traditional vulnerability management approaches have focused on identifying vulnerabilities in isolation, contextual vulnerability management takes a more holistic view, considering the specific context and environment in which vulnerabilities exist. This approach is critical in the age of cloud computing and software as a service (SaaS), where vulnerabilities can have far-reaching impacts.
One key aspect of contextual vulnerability management is contextual vulnerability assessment. This involves analyzing vulnerabilities within the context of the specific environment in which they exist, including the software and hardware components, the network infrastructure, and the organizational policies and processes. By understanding the specific context of a vulnerability, organizations can more accurately assess its potential risks and take appropriate action to mitigate them.
Risk assessment
Risk assessment is another critical aspect of contextual vulnerability management. This involves evaluating the potential impact of a vulnerability on an organization’s assets, including its data, systems, and reputation. By understanding the potential consequences of a vulnerability, organizations can prioritize their efforts and allocate resources appropriately to mitigate the most significant risks.
Vulnerability management in software and cloud
In software and cloud computing, contextual vulnerability management is critical. Software vulnerabilities can have widespread impacts, particularly when many organizations or individuals use the software. In the cloud, vulnerabilities in infrastructure or software can affect multiple tenants and users, making it essential to identify and mitigate them quickly.
Effective methodology for vulnerability managment
Effective contextual vulnerability management in software and cloud environments requires a combination of tools, processes, and policies. Some key strategies include:
- Continuous vulnerability monitoring: By continuously monitoring systems and networks for vulnerabilities, organizations can identify and address potential issues before they can be exploited.
- Patch management: Patching vulnerabilities as soon as patches become available is critical to maintaining the security of systems and networks. This requires effective processes for identifying and testing patches and deploying them to systems and networks.
- Threat intelligence: By staying up to date on the latest threats and vulnerabilities, organizations can be better prepared to identify and mitigate potential risks. Threat intelligence can be gathered from various sources, including industry alerts, security blogs, and government agencies.
- Vulnerability analysis: Analyzing vulnerabilities in depth can help organizations understand their potential risks and identify appropriate mitigation strategies. This can involve a technical analysis of the vulnerability itself and an understanding of the specific context in which it exists.
- Network security: Ensuring the security of networks is crucial to protecting against vulnerabilities. This can involve implementing firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and other security controls and following best practices for securing networks.
Overall, contextual vulnerability management is key to protecting software and cloud infrastructure from potential threats. Organizations can more effectively assess and mitigate their risks by considering the specific context and environment in which vulnerabilities exist. This requires a combination of tools, processes, and policies and a focus on continuous monitoring, patch management, threat intelligence, vulnerability analysis, and network security.
How can Phoenix Security Platform help?
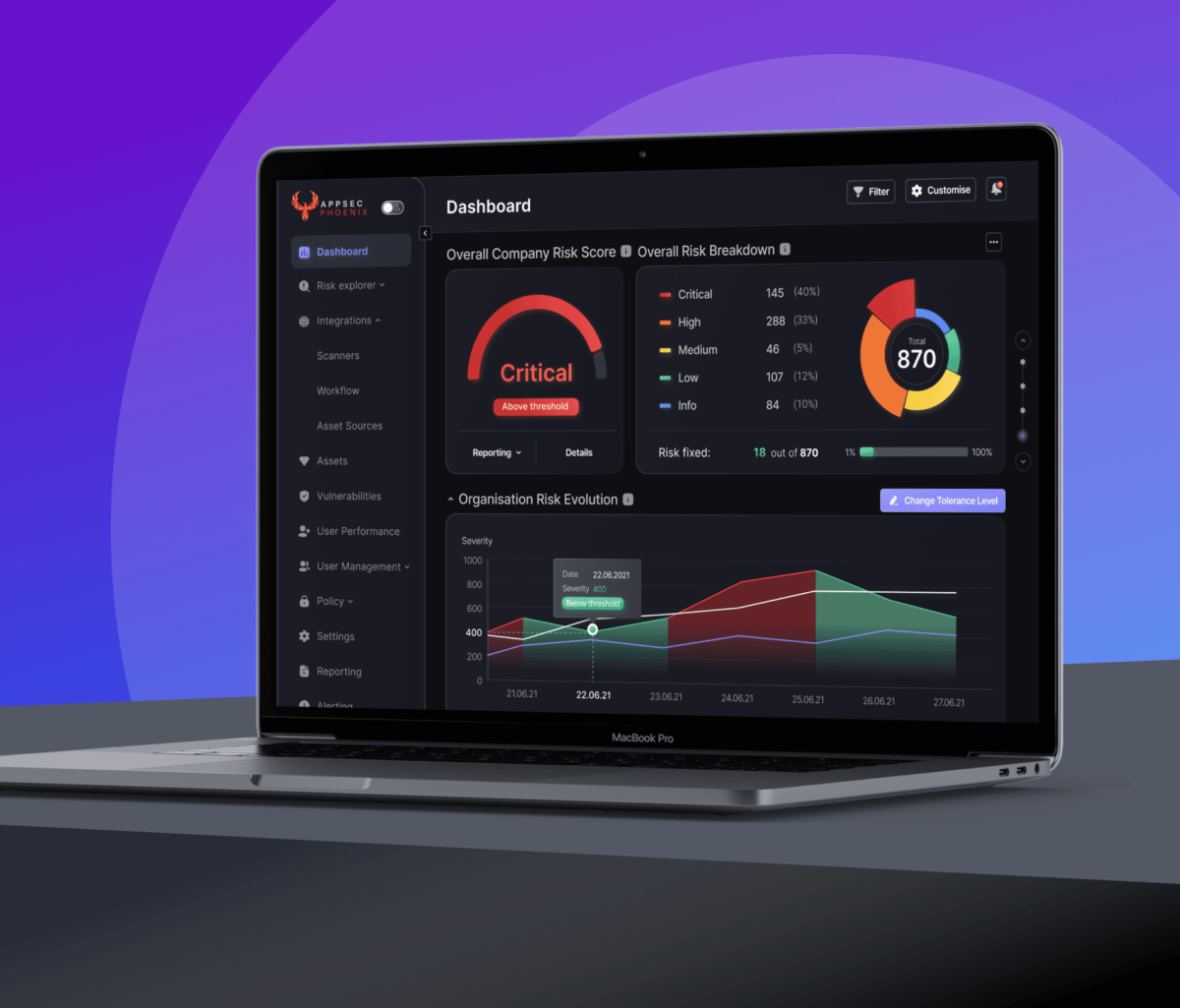
Technology is not the holy grail or answer to all the problems. Vulnerability management remains a people & culture, process, and technology problem.
Phoenix security cloud platform can help automate, correlate and track maturity at scale and facilitate the enforcement of measurements.
Phoenix offers a way to scale triaging and prioritising vulnerabilities, removing the manual part of security analysis and enabling the security team to scale better, from a 1:10 to 1:40 ratio, react faster (from 290 days average resolution time to 30) and be more efficient in the time spent on each vulnerability.
With a proven methodology adopted by over 1000 Security professionals, Phoenix enables security engineers to communicate more effectively with the business in terms of risk and loss and automatically prioritise vulnerabilities for developers.