The new cvss preview CVSS V4 has been released, while the previous version, CVSS version 3.1 was published on June 10, 2019. FIRST announced CVSS’s introducing several changes summarized in Dave Dugal presentation. CVSS 4 make a lot of progress on some of the inflexible variables and the contextual aspect of the metrics. There has been a lot o attention on IoT and Operational Technology with descriptions of attack tactics.

Contents
ToggleCVSS v1
The US National Infrastructure Advisory Council (NIAP) worked through 2003/2004 to come up with a framework that would provide a standard for severity ratings of vulnerabilities in software. The result, CVSSv1, was first released in 2005 and handed off to the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams to maintain moving forward. CVSSv1 was widely viewed as having significant issues, and work began immediately on its successor, CVSSv2.
CVSS v2
CVSSv2 launched in 2007, and was widely adopted by vendors and enterprises as a common language by which to compare software vulnerabilities. Despite wide adoption, v2 also had significant issues to be addressed, so after 5 years of use, work began on CVSSv3.
CVSS v3
Work on CVSSv3 began in 2012, with the 3.0 revision released in 2015. The most recent revision, CVSSv3.1, was released in mid-2019.
A major critique of CVSS v3
In the past years from the release of CVSS there have been several critiques and followup with FIRST on CVE and CVSS, the more prominent one was around the CVE score being all overly critical and exhausting
- CVSS Base Score being used as the primary input to risk analysis
- Not enough real-time threat and supplemental impact details represented
- Only applicable to I.T. systems
- Health, human safety, and industrial control systems are not well represented
- Scores published by vendors are often High or Critical (7.0+)
- Insufficient granularity – fewer than 99 discrete CVSS scores in practice
- Temporal Metrics do not effectively impact the final CVSS score
- The math seems overly complicated and counterintuitive
How is CVSS V3 calculated?
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard designed to assess the severity of security vulnerabilities in computer systems. It provides a way to capture the principal characteristics of a vulnerability and produce a numerical score reflecting its severity. The numerical score can then be used to make informed decisions about prioritising the response to incidents and vulnerabilities in a given system.
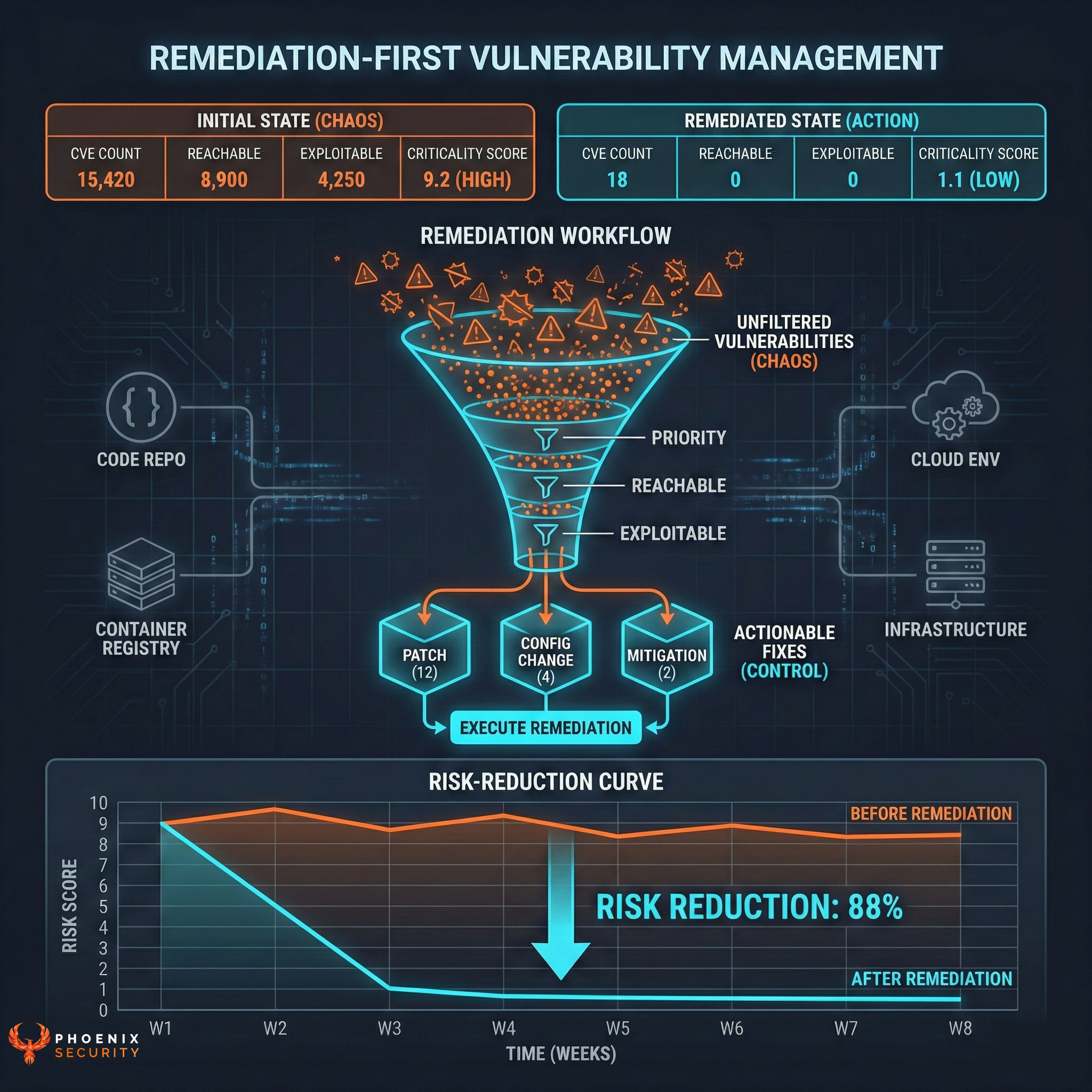
CVSS scores range from 0.0 to 10.0, with 10.0 being the most severe. The score is composed of three metric groups: Base, Temporal, and Environmental.
- Base Metrics capture the characteristics of a vulnerability that are constant over time and across user environments. They include metrics like Attack Vector, Attack Complexity, Privileges Required, User Interaction, Scope, Confidentiality Impact, Integrity Impact, and Availability Impact.
- Temporal Metrics reflect the characteristics of a vulnerability that may change over time but not across user environments. They include Exploitability, Remediation Level, and Report Confidence.
- Environmental Metrics represent the characteristics of a vulnerability that are relevant and unique to a particular user’s environment. They include Collateral Damage Potential, Target Distribution, Confidentiality Requirement, Integrity Requirement, and Availability Requirement.
CVSS Base score has been widely used in our industry, while temporal was rarely used
What is new in CVSS 4
CVSS v3 has faced criticisms on the complexity, lack of clarity, and limitation in contextualisation and prioritisation. CVSS v4 possibly introduces even more complexity but drops some of the most criticized elements.
Some of the elements in the new CVSS can be used in decision threes refer to this article to see some further analysis on decision three vs risk formula
The main updates and enhancements in CVSS v4.0 include:
- Increased simplicity and clarity: The goal of CVSS v4.0 is to simplify the scoring process and eliminate ambiguity by providing clearer guidance and definitions for metrics. This version fine-tunes the ideas of “Attack Complexity” and “Attack Requirements,” making the scoring process more understandable. These changes assist in more precise vulnerability assessment and ensure uniformity among various organisations.
- Amplified adaptability and flexibility: CVSS v4.0 introduces a variety of new metrics and a modular structure, allowing organisations to customize the scoring system to their specific needs and circumstances. This version includes metrics related to operational technology and safety and makes distinctions between active and passive user interaction, allowing for a more detailed vulnerability evaluation in a range of situations. This adaptability leads to a more accurate representation of risk for a specific organization.
- Enhanced depiction of real-world risk: CVSS v4.0 better represents a vulnerability’s actual risk. It considers additional factors such as the probability of exploitation and the potential consequences of a successful attack. This version emphasises including threat intelligence and environmental metrics in scoring, resulting in a more realistic risk evaluation. The introduction of new concepts like “Automatable,” “Recovery,” and “Mitigation Effort” add more nuance to the understanding of each vulnerability.
To start a comparison, we used the base score to compare as most of the cvss in the wild have only a base score specified (approximately 73%)
Some interesting data
- The majority of vulnerabilities in the current database have Attack vector as network specified; that seems to be a trend for all the vulnerabilities that are more at risk of exploitation as the attack vector is remote.
- Those vulnerabilities will be likely translate in remote exploitable in CVSS 4
- During the transition phase, CVSS 3 and CVSS 4 will likely to be similar or retro compatible and the vendor will use factors that are compatible in the two versions.
- Attack Complexity, a metric often misunderstood, is now replaced with attack requirements in v4. During the public preview Dave Dugal, acknowledged this and the proposal suggests splitting the metric by adding “Attack Requirements.”
To see how Phoenix overcomes some of the shortcomings and contextual, location and absence of risk of cvss in: Phoenix Security Risk
CVSSv3 Scoring Scale vs CVSSv2
CVSSv2 qualitative scoring mapped the 0-10 score ranges to one of three severities:
- Low – 0.0 – 3.9
- Medium – 4.0 – 6.9
- High – 7.0 – 10.0
With CVSSv3, the same 0-10 scoring range is now mapped to five different qualitative severity ratings:
- None – 0.0
- Low – 0.1 – 3.9
- Medium – 4.0 – 6.9
- High 7.0 – 8.9
- Critical – 9.0 – 10.0
With CVSSv4, the same 0-10 scoring range would mantain the same scoring
- None – 0.0
- Low – 0.1 – 3.9
- Medium – 4.0 – 6.9
- High 7.0 – 8.9
- Critical – 9.0 – 10.0
CVSS 3 to CVSS 4 mapping
Comparing the two calculators, CVSS V3 Calculator and CVSS V4 Calculator, we analyse a vulnerability with the following vectors:
CVSS:4.0/AV:A/AC:L/AT:P/PR:L/UI:A/VC:H/VI:H/VA:H/SC:N/SI:N/SA:N
In CVSS 4.0 would result in 5.4 -> Medium
(considering that not setting several parameters and comparing basic to basic)
A vector with parameters AV:A/AC:L/PR:L/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
In cvss 3 would result in a 7.4 -> high
Context, Location, Exploitability, probability of exploitation
All the past years’ critique to cvss, like location, exploitability, and probability of exploitation, are still there. CVSS still expresses a point-in-time view of the exploit availability and how dangerous an exploit could be.
Those issues are still very much present in cvss 4 and currently not addressed CVSS V4 seems to remain complex with some improvement on vector and attack path.
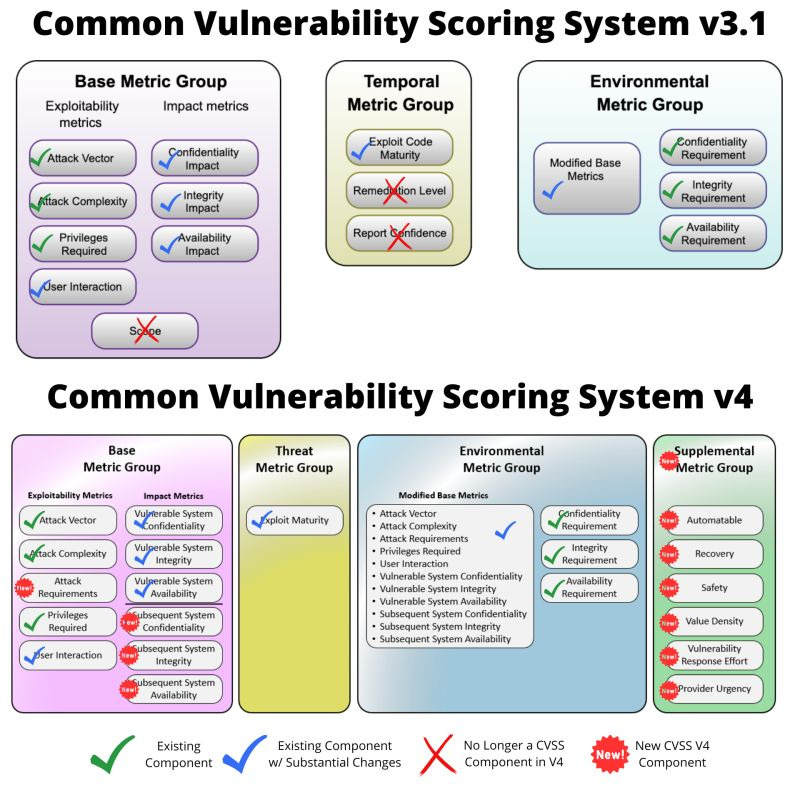
CVSS V3 and V4 differences Credit to patrick garrity
Threat Metric groups like the exploit maturity and environmental metrics expansion are a game forward and expansion of the CVSS formula.
The supplemental metric (optional) are as well a great advancement in the formula and could play a role on the easiness of exploitation.
CVSS 4.0 in Application Security
The CVSS metrics seem more applicable to built libraries and artefacts. They remain distant from application security as they are missing the nuance required to express code and nuances of reachability in a file/library, context, and impact outside basic CIA impact.
Conclusion
CVSS 4 is an advancement from CVSS v3.1 and is in preview, so there might be further changes. As we saw with CVSS 2->3, the implementation lead time is quite long. The impact on application security is still somehow distant and vague, as the CVSS seems to be focused mostly on infrastructure and OT-type of vulnerabilities. Location, Business context is still absent or vaguely touched with CIA scores. There has been quite an improvement in the flexibility and modifiability of the scores.