Introduction
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and organizations are struggling to keep up with the ever-evolving threats. Vulnerability management is essential to any cybersecurity strategy, as it helps identify and address vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. Traditional vulnerability management approaches have focused on identifying and patching vulnerabilities in systems and applications. However, this approach can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, as organizations often have many vulnerabilities to address and limited resources for patching them all. Recently, a risk-based vulnerability management approach has gained popularity due to its ability to prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on the organization’s business objectives.
What is Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
Risk-based vulnerability management is an approach that prioritizes vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on the organization’s business objectives. This means that vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk to the organization are addressed first. In contrast, lower-risk vulnerabilities may be addressed later or accepted as part of the organization’s risk management strategy. The risk-based approach involves evaluating the potential impact of a vulnerability on the organization, taking into account factors such as the criticality of the system, the data it contains, and the potential impact on business operations.
The risk-based approach to vulnerability management is becoming increasingly popular, and it has several benefits over traditional vulnerability management approaches. Firstly, it enables organizations to use their limited resources more efficiently by prioritizing vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk. Secondly, it gives organisations a better understanding of their cybersecurity risks and enables them to communicate them more effectively to key stakeholders. Finally, it aligns vulnerability management efforts with the organization’s business objectives, ensuring that cybersecurity risks are addressed to support its overall goals.
Gartner’s View on Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
Gartner is a leading research and advisory company that provides insights into the technology industry. According to Gartner, the risk-based vulnerability management approach is more successful than pure SLA-based or CVSS-based approaches. The CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) is a widely used framework for assessing the severity of software vulnerabilities. It assigns a score to each vulnerability based on factors such as the access required to exploit the vulnerability, the impact of the vulnerability, and the complexity of the exploit. However, Gartner argues that the CVSS-based approach is limited because it does not consider the context of the vulnerability, such as the business criticality of the system or the data it contains.
Similarly, Gartner argues that SLA (Service Level Agreement)-based approaches, which are based on meeting specific service level targets, are ineffective because they do not adequately measure risk. Gartner recommends a risk-based approach to prioritize and manage vulnerabilities that considers the vulnerability’s context and potential impact on the organization’s business objectives.
How to deploy a mature risk-based vulnerability assessment
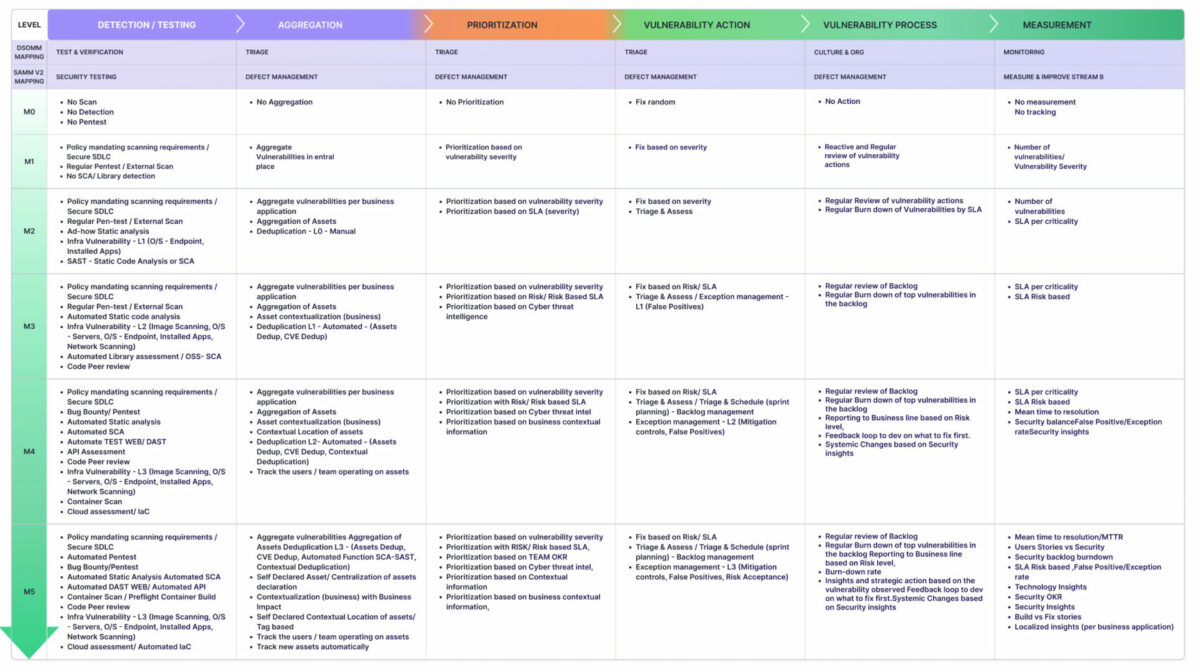
You can leverage the vulnerability maturity assessment framework to assess your organization’s maturity against industry standard. More details in this blog: https://phoenix.security/vulnerability-management-framework/
What is contextual Risk-Based vulnerability
Contextual vulnerability management is a comprehensive approach to identifying, analyzing, and mitigating software and cloud infrastructure vulnerabilities. We have written extensively on the power of prioritization and contextualization. Gartner has also recently published several articles on the power of risk-based vulnerability management.
What elements are used to calculate risk
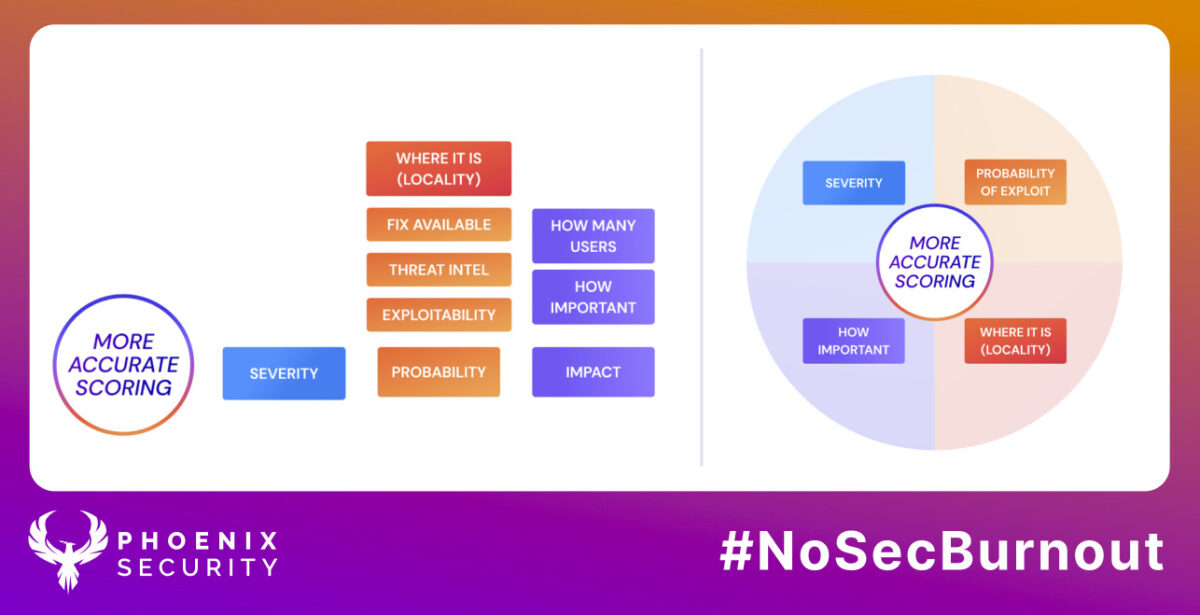
In risk management, we have three main factors
- The probability of exploitation can be derived from
- Location o an asset (internal/ external) where the vulnerability is manifested
- Likelihood of exploitation
- EPSS and the likelihood of exploitation
- Cyber threat intelligence like VulnDB, CISA KEV, Local Advisories
- Dangerousness of the exploit
- Is the exploit a Remote Code Execution (RCE)
- Is there an exploit available for the vulnerability?
- Is the exploit-module automated / readily available in exploitdb, github, nuclei, metaexploit
- The base danger of the exploit is generally communicated by CVSS/ CWSS score.
- The impact of a vulnerability overall
- How many users it impacts
- How much can the organization survive with an application compromised
- How much data is there to compromise
- How private is the data in the application (sensitive, critical etc…)
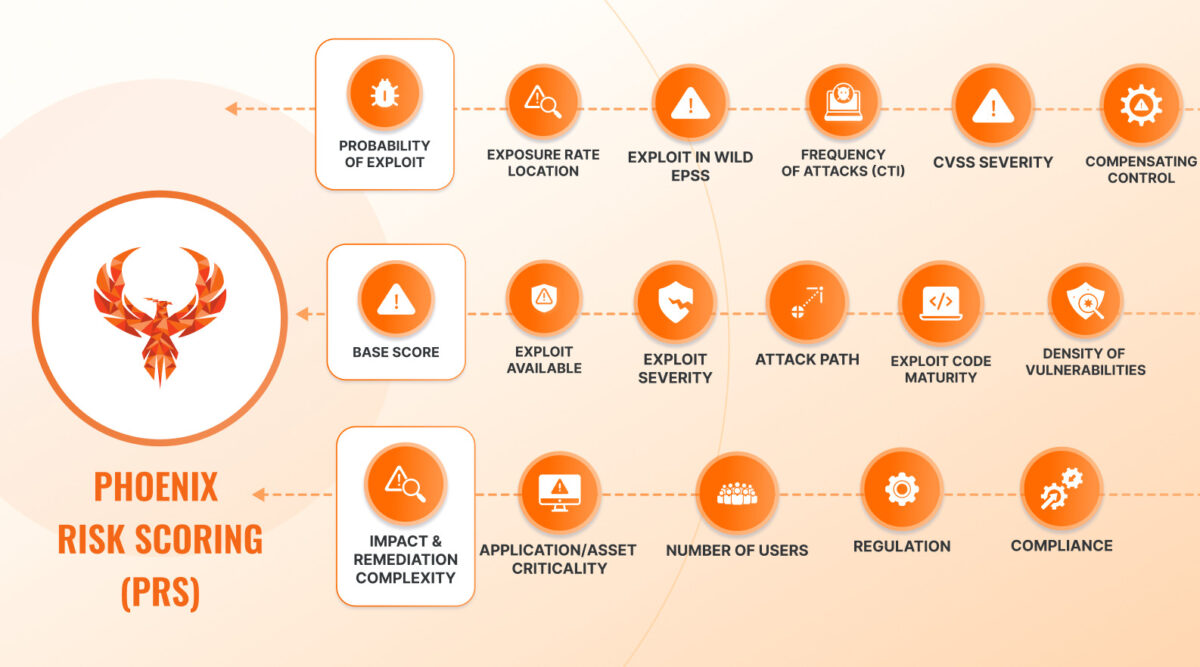
Applying Risk-based Vulnerability Assessment – an example
An example of this approach is the following picture out o a few blog posts this one and this other from Chris Hughes got a lot of attention.
Credit Ingmar Vis
Only a small percentage of vulnerabilities are exploitable, and even fewer in the context of a specific application.
An example:
Application XYZ has 9 CVE 10.
Most security tools nowadays would spit out vulnerabilities with threat level 9 or higher. The list of CVE’s in FictoApp is in the comments.
If implemented correctly, even using just one of the parameters shown above (EPSS) a risk-based vulnerability maturity project can significantly help refocus on the vulnerabilities that matter most (full story and link to the blog post here)
Using EPSS score as an example of exploitability can reduce the vulnerabilities that require attention to 6 or even less.
Bucketing the vulnerabiity exploitation between EPSS-scores: <1%, <10%, <50%, <75%, >75%
Advantages of using a Risk-based Vulnerability management approach
Risk-based vulnerability management provides several benefits over traditional vulnerability management approaches.
- Improved Focus on High-Priority Vulnerabilities
Organizations can first focus on addressing the most critical vulnerabilities by prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on business objectives. This can help organizations reduce their cybersecurity risk more effectively and use limited resources better.
- Better Alignment with Business Objectives
A risk-based approach to vulnerability management can help organizations better align their cybersecurity strategies with their overall business objectives. By considering the potential impact of vulnerabilities on business objectives, organizations can more effectively communicate the importance of vulnerability management to key stakeholders and ensure that resources are allocated appropriately.
- More Effective Use of Automated Tools
Automated vulnerability scanning tools are a key component of most vulnerability management strategies. However, these tools can generate many false positives, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive to investigate. A risk-based approach to vulnerability management can help organizations filter out false positives more effectively and focus their efforts on addressing the most critical vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, a risk-based approach aligns vulnerability management efforts with the organization’s business objectives, ensuring that cybersecurity risks are addressed to support its overall goals.
Challenges of Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
Improving Vulnerability remediation with EPSS
While risk-based vulnerability management provides several benefits, it also poses some challenges. Firstly, it requires knowledge of risk and the collection of external parameters. While traditionally, security tools provide a view of potential issues with CVSS or CWSS, a risk-based approach requires a more comprehensive overview of, location, business criticality, probability of exploitation and more contextual factors.
Conclusions
Riks-based vulnerability management is the key to advancing the vulnerability management program on application and cloud security
SLA and vulnerability severity are antiquated methods that do not provide the tools for a mature vulnerability management program anymore.
How can Phoenix Security Help
Poenix security leverage the power of Cyber threat intelligence, EPSS, Location and business context, to calulate the risk exposure of vulnerabilities and applications in real time.
Phoenix security also allows a risk based approach on SLA, and other traditional parameters. No matter where your organization is in the application and cloud security journey phoenix security is here to help.
If you want to know more about Phoenix security and doing vulnerability management at scale, contact us https://phoenix.security/request-a-demo/