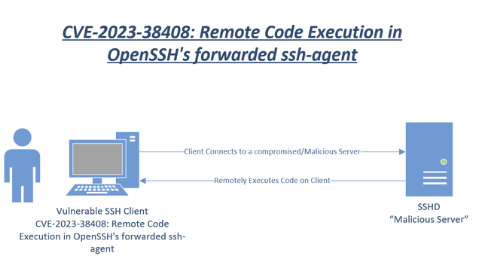
OpenSSH, a widely used suite of networking software, has recently been the subject of security discussions due to a discovered vulnerability. The vulnerability, known as CVE-2023-38408, lies in OpenSSH’s forwarded ssh-agent and can potentially allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary commands. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of this vulnerability, its potential impact, and how to mitigate its risks.
Note: this is a Client-side (SSH Agent), not a server issue. The vulnerability might, later on, affect the server side. Moreover, the exploitation being remote would still require interaction client-server
About OpenSSH’s Agent Forwarding
SSH agent forwarding is a feature of SSH that uses the ssh-agent program to hold private keys for public key authentication. This reduces the need for regular passphrase input, making it instrumental in automation scripts or tasks requiring frequent server connections. The ssh-agent operates by storing keys in memory and unloading only when the process ends. The connections to ssh-agent may be forwarded from further remote to avoid the need for authentication data to be stored on other machines. Despite its benefits, it’s crucial to secure the keys with robust passphrases.
Contents
ToggleThe OpenSSH Vulnerability CVE-2023-38408
The OpenSSH vulnerability, CVE-2023-38408, is a remote code execution vulnerability in OpenSSH’s forwarded ssh-agent. This vulnerability can allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary commands on a system (client) running a vulnerable version of OpenSSH’s forwarded ssh-agent. The vulnerability was independently verified and a proof-of-concept exploit was developed on installations of Ubuntu Desktop 22.04 and 21.10. Other Linux distributions are likely vulnerable and probably exploitable.
The Impact of OpenSSH Vulnerability CVE-2023-38408 t
Successful exploitation of this vulnerability allows a remote attacker to execute arbitrary commands on vulnerable OpenSSH forwarded ssh-agent. This poses a significant security risk, especially considering the widespread use of OpenSSH. For a broader context on the importance of addressing such vulnerabilities, consider the recent critical RCE vulnerability in Citrix, as discussed in this article.
How to Migrate the OpenSSH Vulnerability CVE-2023-38408
Upon confirmation of the vulnerability, Qualys engaged in responsible vulnerability disclosure and coordinated with the vendor, OpenSSH, to announce the vulnerability. The disclosure timeline was swift, with the initial advisory sent to OpenSSH on July 6, 2023, and the coordinated release of the patch on July 19, 2023. Security teams must apply patches for this vulnerability promptly to prevent potential exploitation
What is the exploitation of CVE-2023-38408 In the wild
The vulnerability is relatively new, and there is currently no evidence of exploitation in the wild, or exploit at scale. Hence the EPSS score is in line; nonetheless due to the nature of remote, please consider urgently patching systems that are externally facing
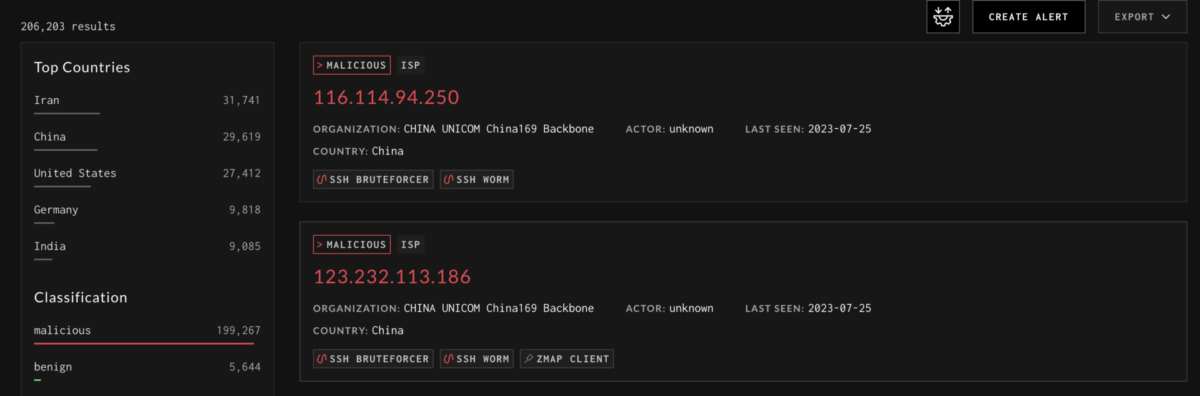
Exploitation with SSH brute-forcing is a common technique adopted so it won’t be short before an attacker will try to weaponize this vulnerability
What is the exploitation data behind CVE-2023-38408 In the wild
CVSS: 4.5 (temp)
CTI interest: 6.11 (mdeium/high)
RCE Type Remote: Yes
Availability: Yes
Status: Proof-of-Concept
EPSS Score: 0.00169
EPSS Percentile: 0.53066
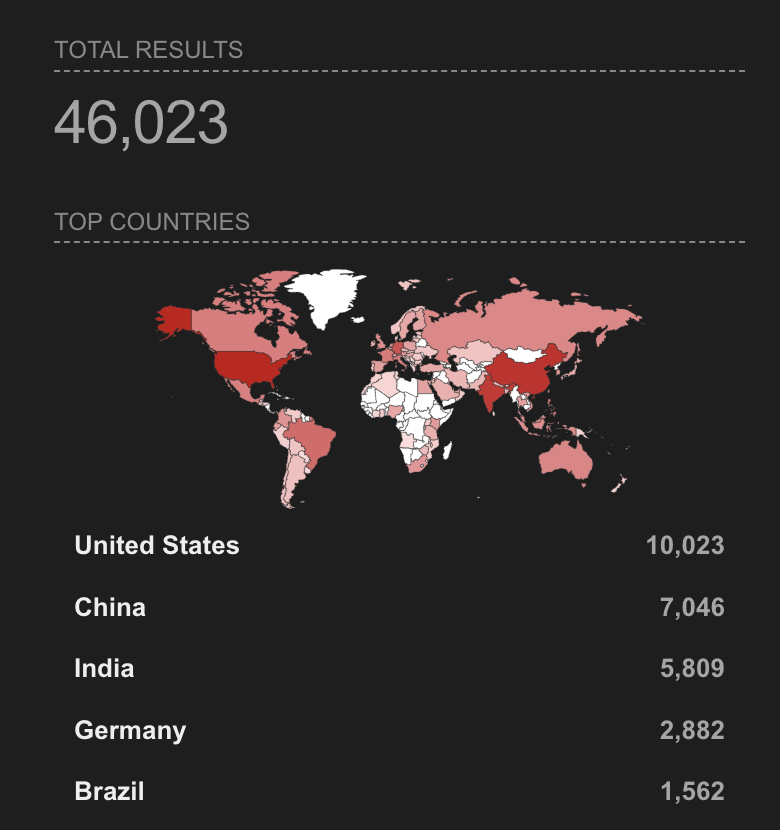
The number of systems with Open SSH agents are around 46K nonetheless the version has not been verified
How to Fix CVE-2023-38408
- While the discovery of CVE-2023-38408 in OpenSSH’s Agent Forwarding is concerning, preventive measures are available to avoid exploitation. If you suspect your system may have been compromised, scanning it for malicious code using tools such as ClamAV, Malwarebytes, or Avast is crucial.
- To effectively address and safeguard against CVE-2023-38408, follow these comprehensive steps:
- Upgrade to OpenSSH 9.3p2 or later
- Upgrading to the latest version of OpenSSH is crucial as it includes critical patches to mitigate the vulnerability. Ensure that all relevant systems and servers are promptly updated to the recommended version or a higher one.
- Restrict PKCS#11 providers
- Configure OpenSSH to allow only specific and trusted PKCS#11 providers. By limiting the use of PKCS#11 providers to known and verified sources, you can reduce the potential attack surface and minimize the risk of exploitation.
- Exercise caution when forwarding SSH agent
- Be cautious when using agent forwarding in SSH. Avoid forwarding your SSH agent to untrusted servers or environments. Evaluate the security implications and only enable agent forwarding when necessary, considering the potential risks associated with CVE-2023-38408.
- Conduct system scans
- Regularly scan your systems using reputable antivirus and malware detection tools like ClamAV, Malwarebytes, or Avast. These scans help identify and mitigate potential threats or any malicious code that may have already affected your system.
- By following these steps, you can effectively mitigate the risks associated with CVE-2023-38408 and ensure the security of your OpenSSH environment. However, it’s important to remember that these measures are part of a larger security strategy. Regular system updates, continuous monitoring, and the use of comprehensive security solutions like Phoenix Security’s Vulnerability Management and Asset Management tools are crucial in maintaining a robust and secure digital infrastructure.
Twitter and other useful resources to fix CVE-2023-38408
################################
— mRr3b00t (@UK_Daniel_Card) July 25, 2023
CVE-2023-38408: Remote Code Execution in OpenSSH's forwarded ssh-agent
################################
now.. first questions…
how many devices in your enterprise do you have running a vulnerable version of SSH?
How many of these are internet…
How Phoenix Can Help
To manage and prevent such vulnerabilities, comprehensive security solutions are essential. Phoenix Security offers tools such as Vulnerability Management and Asset Management to help organisations quickly act on vulnerabilities like OpenSSH’s CVE-2023-38408.
Phoenix’s Vulnerability Management tool can help identify and prioritize vulnerabilities, providing a clear roadmap for remediation. It can help organizations understand the severity of vulnerabilities like CVE-2023-38408 and prioritize their remediation efforts accordingly.
The Asset Management tool, on the other hand, provides a comprehensive view of all assets in an organization’s network. This can help organizations understand which assets are vulnerable to CVE-2023-38408 and need immediate patching.
Conclusion
The discovery of the OpenSSH’s Agent Forwarding CVE-2023-38408 vulnerability underscores the continuous need for rigorous security measures and immediate response. Even robust systems like OpenSSH can harbor hidden vulnerabilities. Proactively rectifying such vulnerabilities through actions such as implementing patches and using comprehensive security solutions like those offered by Phoenix Security is critical to maintaining the integrity of digital assets.
Get in control of your Application Security posture and Vulnerability management
Previous Issues of Vulnerability Weekly
- Movit Transfer Zellis Data Breach
- Latest Security Vulnerability of the Week 24/10/22
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 3/10/22 – Application Security – Cloud – Vulnerability – Exchange Zero Day & Mitigations, bitbucket, cobalt stike
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 12/09/22 – Application Security – Cloud Security – Linux Malware, Windows patched 64 vulns with zero-day, Uber Hack Timeline, GTA 6/Rockstar Hack – This week we deep dive into Linux Malware, Windows patched 64 vuln with zero day, Uber Hack Timeline, GTA 6/Rockstar Hack
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 12/09/22 – Application Security – Uber Hack Timeline – Special Focus on Uber latest news on hack