Previous Issues of vulnerability Weekly
- Latest Security Vulnerability of the Week 24/10/22
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 3/10/22 – Application Security – Cloud – Vulnerability – Exchange Zero Day & Mitigations, bitbucket, cobalt stike
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 12/09/22 – Application Security – Cloud Security – Linux Malware, Windows patched 64 vulns with zero-day, Uber Hack Timeline, GTA 6/Rockstar Hack – This week we deep dive into Linux Malware, Windows patched 64 vuln with zero day, Uber Hack Timeline, GTA 6/Rockstar Hack
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 12/09/22 – Application Security – Uber Hack Timeline – Special Focus on Uber latest news on hack
- Security Vulnerability Weekly 22/08/22 – Apple Vulnerability, Android Bugdrop Vulnerability, WordPress, CISA, and recent Hacks to Mailchimp and Twilio – Apple Vulnerability, CISA new vulnerability for September, Bugdrop new android vulnerabilities, recent hacks to twilio exposing digital ocaean clients and Mailchimp hack
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 08/08/22 – Atlassian Hardcoded Credentials, Sonicwall GSM, Cisco Nexus, Microsoft Macro, Vmware Fix, Mac OS spotlight vulnerability and more
Italian Cybersecurity agency warns hacker exploiting two years old vulnerability at scale
On February 4th Italian agency, together with the Computer Emergency Response team from France have warned of a campaign to attack Vmware servers systematically
“These attack campaigns appear to exploit CVE-2021-21974 the Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT) of France said in an advisory on Friday.
The related VMware Esxi advisory
https://www.vmware.com/security/advisories/VMSA-2021-0002.html
A patch for those vulnerabilities has been available since February 23, 2021.
CERT-FR strongly recommends applying the patch as soon as possible but adds that systems left unpatched should also be scanned to look for signs of compromise.
CVE-2021-21974 affects the following systems:
- ESXi versions 7.x prior to ESXi70U1c-17325551
- ESXi versions 6.7.x prior to ESXi670-202102401-SG
- ESXi versions 6.5.x prior to ESXi650-202102101-SG
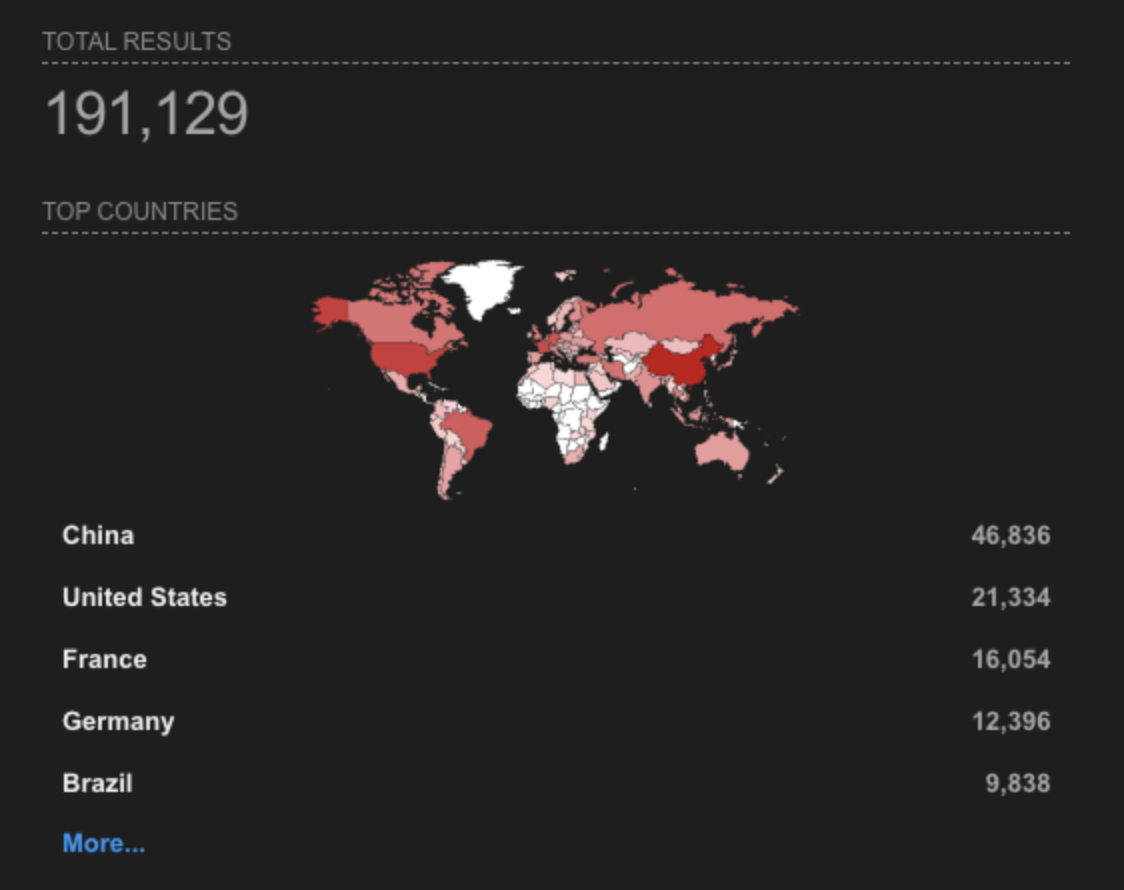
Currently, there are 191,129 systems exposed on the web
Criticality Analysis
The system attacked in the recent ransomware attack were even more vulnerable as some of them were directly exposed over the web or with a secondary connection to the web system.
How old was the vulnerability? old… almost 2 years CVE-2021-21974
Curently, EPSS gives this at 0.12 % of exploitability.
“cve”:”CVE-2021-21974″,”epss”:”0.123880000″,”percentile”:”0.951510000″,”date”:”2023-02-06″
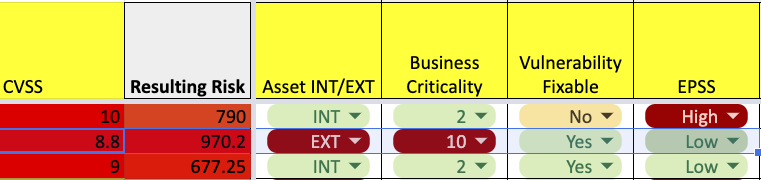
The current scoring for those vulnerabilities is: CVSS 8.8. Currently could be overshadowed by other critical vulnerabilities that are not that critical.
Even with a low EPSS score but the external and critical system, the vulnerability should overshadow a CVSS 9/10 with low criticality and not facing externally.
As an added value, this falls under the 95% percentile of the scored EPSS data.
Is just exploitability a driving factor? Those systems were critical and externally exposed, making them low-hanging fruit for remediation…, but they were not remediated.
Using a quick, simplified calculation is clear to see that even a system with a low EPSS exploitability score but a high percentile could get overshadowed by other internal systems with higher CVSS.
In this case, though, the Phoenix Vulnerability risk scoring would have bumped up the risk level of the CVSS 8.8 for crucial systems like VMware hosts/hosts and external or DMZ-facing systems.
Vmware Ransom
In its alert released then, VMware described the issue as an OpenSLP heap-overflow vulnerability that could lead to the execution of arbitrary code. “A malicious actor residing within the same network segment as ESXi who has access to port 427 may be able to trigger the heap-overflow issue in OpenSLP service resulting in remote code execution,” the virtualisation services provider noted.
“Notably, the group behind the Nevada Ransomware is also buying compromised access by themselves, the group has a dedicated team for post-exploitation and for conducting network intrusions into the targets of interest.”
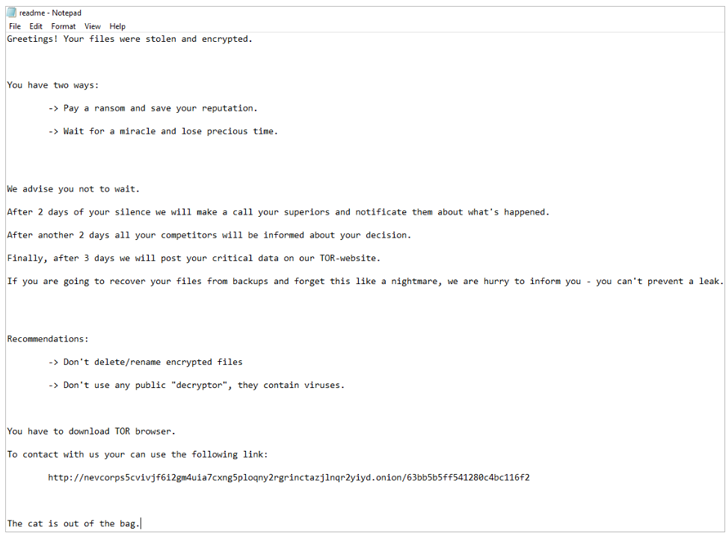
Ransomware note from Hacker News
However, Bleeping Computer reports that the ransom notes seen in the attacks bear no similarities to Nevada ransomware, adding the strain is being tracked under the name ESXiArgs.
When the server is breached, the following files are stored in the /tmp folder:
- encrypt – The encryptor ELF executable.
- encrypt.sh – A shell script that acts as the logic for the attack, performing various tasks before executing the encryptor, as described below.
- public.pem – A public RSA key used to encrypt the key that encrypts a file.
- motd – The ransom note in text form that will be copied to /etc/motd so it is shown on login. The server’s original file will be copied to /etc/motd1.
- index.html – The ransom note in HTML form that will replace VMware ESXi’s home page. The server’s original file will be copied to index1.html in the same folder.
For more info refer to Ransomware article on bleeping computer:
Get in control of your Application Security posture and Vulnerability management
Previous Issues of vulnerability Weekly
- Latest Security Vulnerability of the Week 24/10/22
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 3/10/22 – Application Security – Cloud – Vulnerability – Exchange Zero Day & Mitigations, bitbucket, cobalt stike
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 12/09/22 – Application Security – Cloud Security – Linux Malware, Windows patched 64 vulns with zero-day, Uber Hack Timeline, GTA 6/Rockstar Hack – This week we deep dive into Linux Malware, Windows patched 64 vuln with zero day, Uber Hack Timeline, GTA 6/Rockstar Hack
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 12/09/22 – Application Security – Uber Hack Timeline – Special Focus on Uber latest news on hack
- Security Vulnerability Weekly 22/08/22 – Apple Vulnerability, Android Bugdrop Vulnerability, WordPress, CISA, and recent Hacks to Mailchimp and Twilio – Apple Vulnerability, CISA new vulnerability for September, Bugdrop new android vulnerabilities, recent hacks to twilio exposing digital ocaean clients and Mailchimp hack
- Security Vulnerability of the Week 08/08/22 – Atlassian Hardcoded Credentials, Sonicwall GSM, Cisco Nexus, Microsoft Macro, Vmware Fix, Mac OS spotlight vulnerability and more