Hello, everyone. Frank here with a quick analysis of the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) top routinely exploited vulnerabilities 2023 over the years. Recently, an update for 2022 to 2023 revealed some compelling trends that warrant a closer look. Let’s dive into the evolving landscape of application security and vulnerability management.
Full Video Analysis:

Contents
ToggleThe Changing trends and vendor distribution in CISA Top Exploited Vulnerabilities 2023
From 2022 to 2023, the number of top routinely exploited vulnerabilities highlighted by CISA KEV expanded significantly. In 2022, the report listed 30 vulnerabilities, 12 of which were the most exploitable. By 2023, the number had grown to 50, with 15 in the top exploitable category. This increase underscores the growing challenge of securing a rapidly diversifying technology landscape.
You can interact with the diagrams above in the first link, and if you want to explore more, you can visit the other intelligence that powers Phoenix Security CTI.
- CISA KEV: https://phoenix.security/what-is-cisa-kev-main/
- Exploit in the wild: https://phoenix.security/what-is-exploitability/
- OWASP/Appsec Vulnerability: https://phoenix.security/what-is-owasp-main/
- CWE/Appsec Vulnerabilities: https://phoenix.security/what-is-cwe-main/
Shifting Vendor Density and Exploitation Methods in CISA Top Routinely Exploited 2022
While Microsoft previously dominated the focus in 2022—with vulnerabilities in Exchange and Microsoft Services frequently targeted—2023 showed a more distributed attack surface across multiple vendors. Notable contributors included Atlassian, Juniper, and Ivanti, alongside Microsoft. This shift highlights the expanding range of technologies targeted by malicious actors and the necessity for organizations to adopt robust application security posture management (ASPM) solutions.
Vendor Trends
In 2022, Microsoft vulnerabilities accounted for a significant portion of the top exploited list, particularly involving Remote Code Execution (RCE) and Privilege Escalation. By top routinely exploited vulnerabilities in 2023. However, the data reveals a broader distribution of vulnerabilities across vendors:
- Microsoft: Despite a reduction in targeted vulnerabilities in 2023, RCE and authentication bypass remained common attack vectors.
- Atlassian and Apache: Contributed to critical vulnerabilities in Confluence and Log4j, underscoring persistent risks in enterprise collaboration and logging systems.
- Juniper, Cisco, and Ivanti: These infrastructure-focused vendors emerged prominently in 2023, reflecting increased networking and business-critical systems targeting.
Ivanti, in particular, experienced a tough year, with numerous vulnerabilities identified across its product suite. This highlights the growing complexity of securing IT infrastructure at scale.
Exploitation Patterns
A critical component of the CISA KEV analysis is understanding the diverse methodologies employed by threat actors to exploit vulnerabilities. These attack methods are a window into the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) adversaries use to compromise systems. Below is a detailed breakdown of the methodologies and their prevalence:
The exploitation methods haven’t shifted dramatically. Remote Code Execution (RCE), authentication bypass, and privilege escalation remain the top attack vectors. RCE vulnerabilities, in particular, have been repeatedly weaponized for attacks on high-value targets, from ransomware to sophisticated nation-state campaigns.
| Type | Number of vulnerabilities |
| RCE | 25 |
| Authentication Bypass | 6 |
| Privilege Escalation | 5 |
| Arbitrary code execution | 4 |
| Elevation of Privilege | 2 |
| SQL Injection | 2 |
| Server-Side Request Forgery | 2 |
| Server Path Traversal | 2 |
| Heap-based Buffer Overflow | 2 |
| Code Injection | 2 |
| Buffer Overflow | 2 |
| Path Traversal | 2 |
| External Variable Modification | 2 |
| Missing Authentication for Critical Function | 2 |
| Code Execution | 2 |
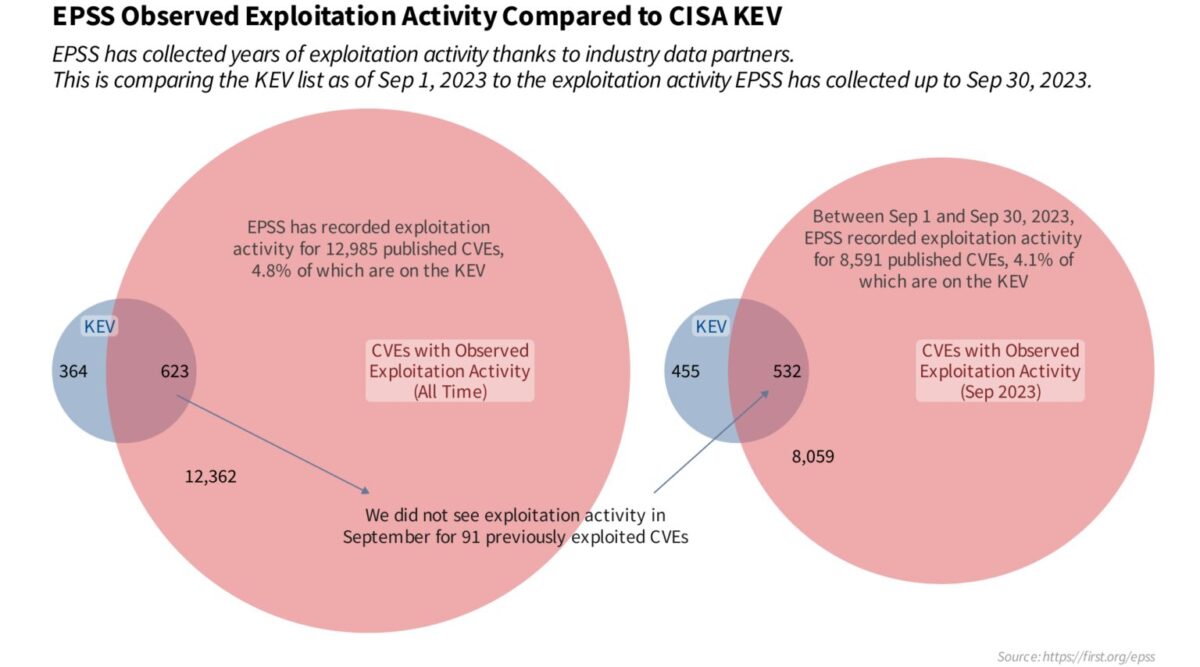
The high Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) scores for these vulnerabilities further emphasize their attractiveness to attackers. What’s striking is how the EPSS scores are spread across the list, showing that the risk is not confined to a few vulnerabilities but distributed broadly. This makes comprehensive vulnerability management more critical than ever.
EPSS Insights: Exploitation Likelihood Across 2022 and 2023 CISA Top Routinely Exploited
The median EPSS scores for the top routinely exploited vulnerabilities 2022 and 2023 reveal an unsettling reality: most vulnerabilities are highly exploitable across the board. For example:
– RCE vulnerabilities in Microsoft’s Exchange Server and Apache’s Log4j remain among the highest risk.
– Authentication bypass flaws in Ivanti’s Endpoint Manager Mobile and Juniper’s Junos OS showcase how attackers continue to exploit access-related weaknesses.
These findings suggest that while organizations have made strides in patching the most critical vulnerabilities, the spread of medium-to-high EPSS scores indicates a broader range of attack vectors requiring attention.
Note that not all the Top routinely exploited vulnerabilities or the one in KEV have an EPSS Value, so using both elements is key in the effort of prioritizing vulnerabilities with Phoenix Security. Both drive different values in the risk formula. The topic has been widely discussed here as well
Implications for Application Security and Vulnerability Management
CISA’s expanding KEV list serves as a wake-up call for organizations to prioritize proactive security measures. Here’s what this means for your ASPM strategy:
1. Broader Vendor Coverage: With vulnerabilities now spread across more vendors and sectors, organizations must expand their focus beyond Microsoft and Apache to include networking and infrastructure solutions like Juniper and Cisco.
2. Prioritization Through Context: EPSS scores and real-time threat intelligence should guide vulnerability prioritization. Not all vulnerabilities carry equal risk, and focusing on those with high EPSS scores ensures efficient resource allocation.
3. Secure SDLC Practices: Vendors must embrace secure-by-design principles, reducing classes of vulnerabilities at the development stage to mitigate the growing attack surface.
4. Collaboration With Security Providers: Partnering with ASPM platforms that integrate data from CISA KEV and other threat intelligence sources can streamline remediation efforts and enhance overall security posture.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, the shift in CISA’s KEV data from 2022 to 2023 reflects a changing and increasingly complex threat landscape. The widespread targeting of multiple vendors and technologies underscores the importance of robust application security and vulnerability management strategies.
At Phoenix Security, we’re committed to helping organizations stay ahead of these evolving threats. With our integrated ASPM platform, you can leverage real-time insights from CISA KEV and over 28 other sources to prioritize and mitigate vulnerabilities effectively. Stay safe, and remember to patch those systems regularly!
Get on top of your code and container vulnerabilities with Phoenix Security Actionable ASPM

Organizations often face an overwhelming volume of security alerts, including false positives and duplicate vulnerabilities, which can distract from real threats. Traditional tools may overwhelm engineers with lengthy, misaligned lists that fail to reflect business objectives or the risk tolerance of product owners.
Phoenix Security offers a transformative solution through its Actionable Application Security Posture Management (ASPM), powered by AI-based Contextual Quantitative analysis. This innovative approach correlates runtime data with code analysis to deliver a single, prioritized list of vulnerabilities. This list is tailored to the specific needs of engineering teams and aligns with executive goals, reducing noise and focusing efforts on the most critical issues. Why do people talk about Phoenix

• Automated Triage: Phoenix streamlines the triage process using a customizable 4D risk formula, ensuring critical vulnerabilities are addressed promptly by the right teams.
• Contextual Deduplication: Utilizing canary token-based traceability, Phoenix accurately deduplicates and tracks vulnerabilities within application code and deployment environments, allowing teams to concentrate on genuine threats.
• Actionable Threat Intelligence: Phoenix provides real-time insights into vulnerabilities’ exploitability, combining runtime threat intelligence with application security data for precise risk mitigation.

By leveraging Phoenix Security, you not only unravel the potential threats but also take a significant stride in vulnerability management, ensuring your application security remains up to date and focuses on the key vulnerabilities.