Contents
ToggleWhy AI Agents in Application Security?
Phoenix AI Agents for ASPM and Vulnerability Management can help application security teams manage the overwhelming amount of data they deal with. These teams aren’t short on data—they’re drowning in it. Every scanner floods the backlog with CVEs, misconfigurations, and container issues, most of which have no exploit path or business relevance. Engineers are asked to fix “critical” findings that never touch production, while true risks linger unaddressed.
That imbalance is now colliding with another shift: AI-driven code and AI-driven malware. Engineers use LLMs to accelerate development, but attackers are doing the same to accelerate exploitation. Research shows rogue AI models can generate working exploits for new CVEs in under an hour. Another study demonstrates that malicious LLMs intentionally designed to aid attackers can output full exploitation chains.
In this environment, speed matters. But speed without context is wasteful. That’s where Phoenix Security’s AI Agents step in.

The Phoenix Approach: Agentic AI, Human Aligned
We are launching not one, but three agents to help get from vulnerability to remediation faster and with our upcoming MCP server connect vulnerability remedy in Modern Cursor, Lovable, Github Copilot, and other vibe coding platforms. We are announcing our AI agents with a clear stance: agents should work alongside you, not replace them. The difference is precision. Rather than spraying generic patch suggestions, the Phoenix agents – The Researcher, The Analyzer, and The Remediator – work together to deliver context-driven remediation at scale.
The Researcher
A real-time intelligence engine. It ingests automatically crawl and research vulnerability intelligence CTI, CISA KEV, EPSS scores,
The agent is also trained to identify the pattern in vulnerability that leads to ransomware campaigns, and POC exploit data to highlight which vulnerabilities are weaponized and how they’re being used. It goes beyond CVE summaries, tracing root causes and mapping threat actors to exploited flaws.
The Analyzer
A contextual modeler. It simulates attack paths in an organization’s actual environment, showing which vulnerabilities are reachable, exploitable, and business-critical. Instead of ranking CVEs in a vacuum, it maps real attack surfaces across code, containers, infra, and runtime.
The Remediator
A surgical planner. The agent proposes the remediation bundles by asset, by attack vector and common remediation with insight and context to evaluate the validity of a vulnerability in your context. It transforms intelligence into environment-specific fixes: patching guidance tailored to frameworks, YAML snippets for IaC, compensating controls when no patch exists, and ticket-ready remediation plans already tagged with ownership. Developers get actionable fixes in the tools they use daily—Jira, ServiceNow, IDEs, even MCP servers and future integrations with Cursor.
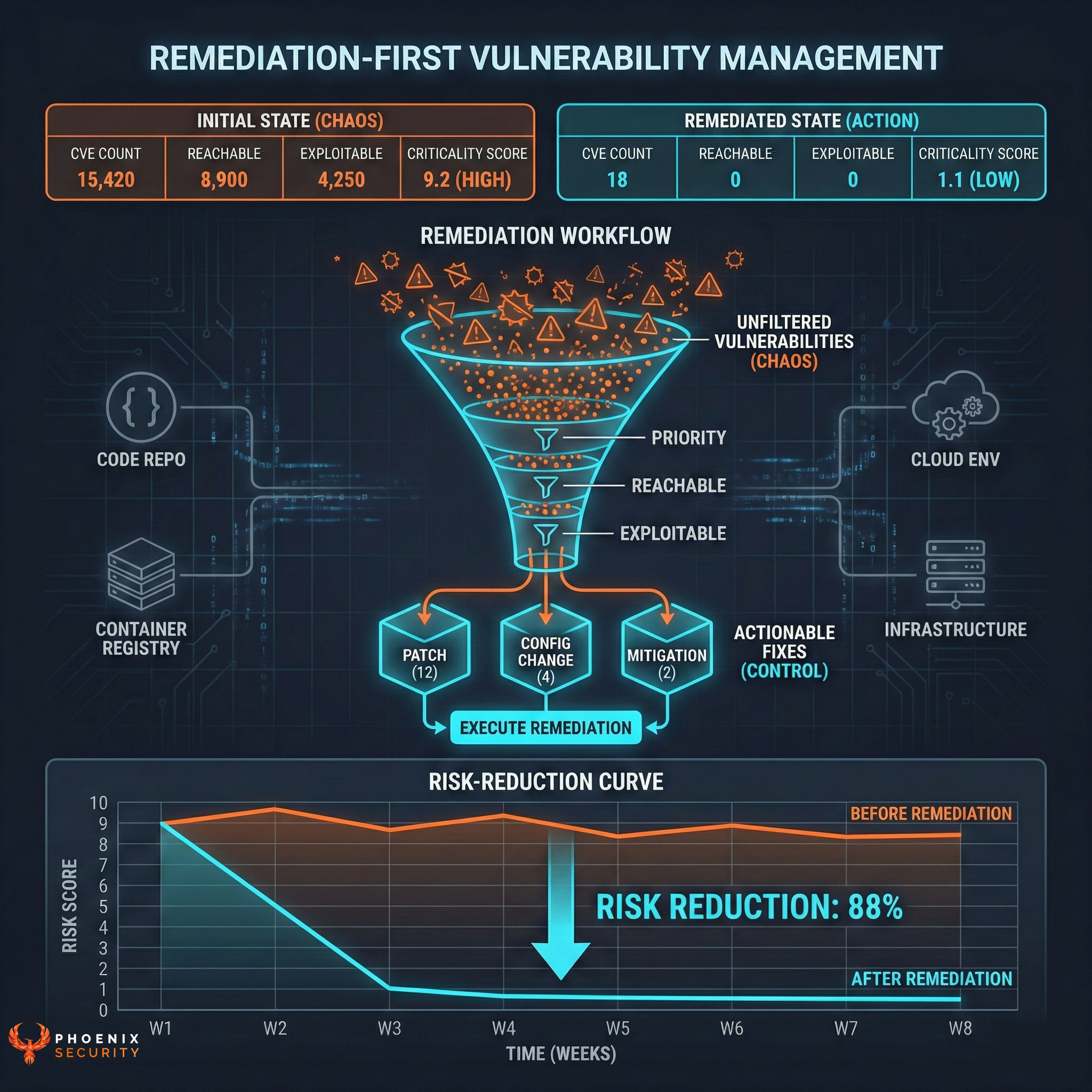
Together, these agents cut through noise and deliver remediation pathways rooted in reachability, exploitability, and business impact.
How it normally works today
In most organizations, the process looks painfully manual. Vulnerability scanners flood dashboards with tens of thousands of findings. Security analysts export reports, attempt to cross-check them with CTI feeds, and try to gauge whether an exploit exists. Weeks can pass before risk is understood. From there, analysts open tickets in Jira or ServiceNow, often stripped of context—“critical CVE, please patch.” Developers receive a backlog of alerts without clarity on reachability, exploitability, or business impact.
The result:
- Analysts spend hours sifting through false positives.
- Developers lose days chasing vulnerabilities that don’t matter.
- Remediation timelines stretch from weeks to months.
- SLA and SLO targets slip, and leadership is left with metrics that don’t reflect reality.
How Phoenix AI Agents change that
The Researcher
Act as a deep diver in vulnerabilities. Instead of analysts combing through threat feeds and CVE databases manually, the Researcher A real-time intelligence engine ingests automatically, crawls and researches vulnerability intelligence CTI, CISA KEV, EPSS scores, intelligence, and POC exploit data continuously. It highlights which vulnerabilities are being actively exploited, which threat actors are using them, and what the likely impact is. Tasks that typically take analysts dozens of hours per week are automated in real time.
The Analyzer
Replaces weeks of manual attack-path modeling. Traditionally, threat modeling is a whiteboard exercise or a spreadsheet-heavy process that can’t keep pace with agile release cycles. The Analyzer simulates attack paths dynamically, across the actual environment—code, containers, infra, and runtime. Instead of relying on generic CVSS scoring, teams instantly see which vulnerabilities are reachable and exploitable. What once took several security engineers a sprint to map is distilled into minutes.
The Remediator
Remediation is usually where the handoff breaks down. The agent proposes remediation bundles by asset, by attack vector and common remediation with insight and context to evaluate the validity of a vulnerability in your context. Tickets are raised with little context, forcing developers to ask: “Where does this vulnerability live? How do I fix it? Does it even matter?” This back-and-forth consumes cycles and creates frustration. The Remediator eliminates that waste by delivering environment-specific fixes: framework-aware patch guidance, YAML snippets for IaC, compensating controls when patches don’t exist, and ticket-ready remediation plans already tagged with ownership.
Developers receive fixes they can apply immediately, in the tools they already use. That alone saves hours of clarification meetings per vulnerability cluster and accelerates MTTR by up to 10x.
The outcome
Together, these agents cut through noise and deliver remediation pathways rooted in reachability, exploitability, and business impact. Instead of analysts drowning in triage and developers chasing irrelevant CVEs, teams act on a curated set of vulnerabilities with context-rich remediation already mapped.
What once required weeks of analyst review, triage, and developer back-and-forth is reduced to a workflow measured in hours or days. That translates directly into SLA compliance, faster MTTR per severity, and millions in reclaimed engineering hours at enterprise scale.
From Visibility to Measurable Reduction: Case Studies

ClearBank
ClearBank engineers were overwhelmed. Phoenix’s agentic approach reduced container vulnerabilities 98% improving time to fix and overall communication with the engineering team. Criticals dropped 96%, and asset attribution hit the maximum. By aligning remediation directly with developer workflows, ClearBank saved $15M in developer time.
Neil Reed, Principal AppSec Engineer, captured it best: “Phoenix helped us move from noise to precision. We now focus on what truly matters—and fix faster than ever before.”
Bazaarvoice
Retail-scale velocity meets security complexity. Within two weeks of implementing Phoenix Security, Bazaarvoice drove all critical vulnerabilities to zero and reduced high-risk findings by 40%. The AI agents enabled direct alignment between engineering and AppSec without adding friction.
Global Ad-Tech
In the high-turnover world of advertising tech, speed is everything. By unifying remediation models across code and cloud, this customer cut container vulnerabilities by 78% and reduced SCA issues by 82%.
These results prove AI agents aren’t theoretical – they are already producing measurable reductions in enterprise environments.
Why Prioritization Without Context Fails
Traditional vulnerability management and even Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) were designed for static infrastructures. They rank risks by CVSS or generalized likelihood but fail to reflect dynamic code-to-cloud reality.
Consider two CVEs with identical “critical” scores. One exists in a legacy test system disconnected from production. The other sits in a production-facing container, reachable through customer-facing APIs. Only the latter matters. Yet traditional tooling treats both as equal.
Phoenix agents correct this imbalance:
- Reachability analysis: Is the vulnerable function actually invoked in runtime?
- Exploitability intelligence: Is a proof-of-concept available? Is it weaponized by ransomware operators?
- Business alignment: Does the system touch customer PII or revenue-generating services?
- Ownership clarity: Which team owns the fix? Which environment is impacted?
This context transforms remediation from endless ticket queues into focused, surgical action.
Remediation as Workflow, Not Alert
Noise reduction is not the goal. The goal is real remediation—and that requires treating remediation as a workflow, not an alert.
Phoenix Security agents embed remediation directly into the engineering process:
- Auto-ticketing with context: Findings routed to Jira or ServiceNow with ownership, exploitability, and environment details pre-tagged.
- SLA/SLO tracking by severity: Monitoring compliance over time, not just at discovery.
- MTTR per severity group: Calculated from when the team was informed, reflecting operational reality.
- Risk reduction metrics: Measuring resolved exploitable and reachable risks, not vanity CVE counts.
These align with insights from industry practitioners:
- “Mean time to resolve from when the team was informed is the most logical metric,” noted James Berthoty.
- Katie Norton highlighted escape rate and vulnerability density as key measurements of program health.
- Chris Romeo emphasized watching MTTR trends as SDL maturity improves.
By embedding these metrics into remediation-aware workflows, Phoenix AI Agents give CISOs a quantifiable story to bring to the boardroom while giving engineers a clear, actionable backlog.
Engineers in the Age of AI-Generated Code and AI-Generated Exploits
Developers today build with LLM copilots at their side. Productivity skyrockets, but so does the chance of insecure patterns slipping into production. Simultaneously, attackers are using rogue AI models to automate exploit creation, shrinking the window from CVE disclosure to weaponization.
The Valmarelox study demonstrated how AI could weaponize a new CVE in under an hour. The rogue LLM paper revealed that specialized malicious models can output full exploitation frameworks. Attackers no longer need deep expertise—they can delegate it to AI.
This accelerates the exploitability curve. Vulnerabilities that once had months before weaponization now face days, even hours. Engineers cannot afford to sift through irrelevant tickets or fix issues in isolation. They need remediation intelligence directly in their IDE, their MCP server, their CI/CD workflow.
Phoenix Security is already prepared for this future, planning integrations that will feed prioritized and deduplicated vulnerabilities into IDEs like Cursor. Engineers will see context-enriched remediation suggestions alongside their code, making secure development seamless.
Why AI Without Context is just a Liability
Not all AI in cybersecurity is created equal. Pointing an LLM at a CVE feed may generate summaries or diagrams, but it lacks the context to drive decisions. Without reachability, exploitability, and ownership mapping, AI creates the illusion of intelligence while generating expensive noise.
The Phoenix difference lies in agentic AI—agents that know what to do next:
- Correlating CTI with runtime reachability
- Simulating attack paths in code-to-cloud topologies
- Generating remediation plans tailored to the environment and team
Context-aware remediation is the safeguard against AI hallucinations. It’s also the only way to make AI outputs actionable at enterprise scale.
The Future of Remediation-Aware ASPM
AI-driven remediation is not the end goal—it’s the enabler of DevSecOps at enterprise scale. With MCP and IDE integration on the horizon, Phoenix Security is closing the loop: from threat intelligence to contextual triage, from attack-path simulation to ticket-ready remediation, and soon, from IDE hints to full agent-assisted secure coding.
This isn’t about replacing engineers or security analysts. It’s about multiplying their impact. Phoenix AI Agents ensure teams spend less time triaging and more time fixing. They don’t just reduce noise—they deliver outcomes: 98% fewer vulnerabilities to chase, 96% fewer criticals in production, and millions in developer hours reclaimed.
For organizations serious about measurable risk reduction, this is the next evolution of ASPM.
Get on top of your code and container vulnerabilities with Phoenix Security Actionable ASPM

Organizations often face an overwhelming volume of security alerts, including false positives and duplicate vulnerabilities, which can distract from real threats. Traditional tools may overwhelm engineers with lengthy, misaligned lists that fail to reflect business objectives or the risk tolerance of product owners.
Phoenix Security offers a transformative solution through its Actionable Application Security Posture Management (ASPM), powered by AI-based Contextual Quantitative analysis. This innovative approach correlates runtime data with code analysis to deliver a single, prioritized list of vulnerabilities. This list is tailored to the specific needs of engineering teams and aligns with executive goals, reducing noise and focusing efforts on the most critical issues. Why do people talk about Phoenix

• Automated Triage: Phoenix streamlines the triage process using a customizable 4D risk formula, ensuring critical vulnerabilities are addressed promptly by the right teams.
• Contextual Deduplication: Utilizing canary token-based traceability, Phoenix accurately deduplicates and tracks vulnerabilities within application code and deployment environments, allowing teams to concentrate on genuine threats.
• Actionable Threat Intelligence: Phoenix provides real-time insights into vulnerabilities’ exploitability, combining runtime threat intelligence with application security data for precise risk mitigation.

By leveraging Phoenix Security, you not only unravel the potential threats but also take a significant stride in vulnerability management, ensuring your application security remains up to date and focuses on the key vulnerabilities.